
Videos (0) bacterial meningitis is inflammation of the layers of tissue surrounding the brain and spinal cord (meninges) caused by bacteria. The diagnosis is based on the results of.
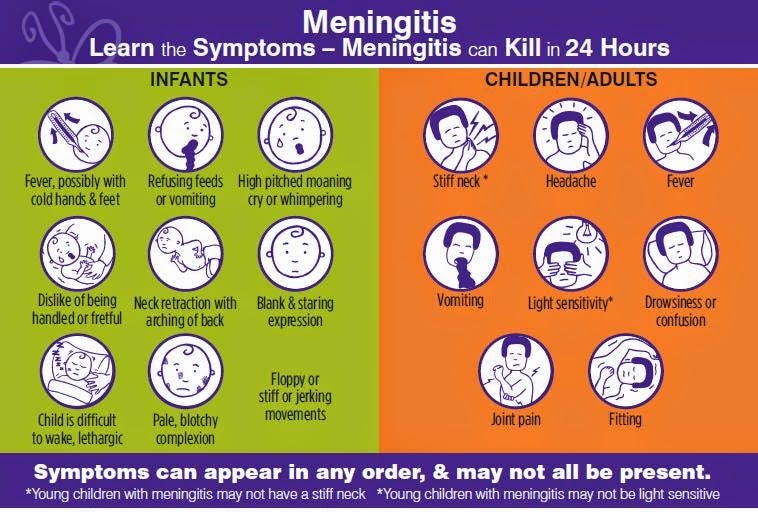
Newborns with bacterial meningitis are usually irritable, vomit, or may have seizures.
Bacterial meningitis in infants. Diagnosis is by cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Bacterial meningitis continues to be an important cause of mortality and morbidity in neonates and children throughout the world. In children under 5 years, including babies over 1 month old, the most common bacteria that cause meningitis are:
The types and distribution of pathogens are related to gestational age, postnatal age, and geographic region. In this study, the mortality of children aged from 2 to 59 months before the introduction of the hib vaccine was 7.1 for 1000 hospitalizations, compared to 8.5 for 1.000 hospitalizations after its introduction. It can affect anyone but is most common in babies, young children, teenagers and young adults (nhs, 2016).
Confirming the diagnosis is difficult. This bacterium is found in the sinuses, nose, and lungs. Meningitis is caused by either a bacterial infection or a viral infection.
Bacterial meningitis can get worse very quickly. Neonatal bacterial meningitis is uncommon but devastating. A retrospective study was performed on 78 patients (newborn to 2 years old) with clinically proved bacterial meningitis.
Bacterial meningitis is inflammation of the lining that surrounds and protects your child�s brain and spinal cord. The most common types that infect babies include: Bacterial meningitis (bm) is a serious condition, presenting a major diagnostic and therapeutic challenge in everyday practice.
The bacteria are found in the mouth, throat, or nose. Group b streptococcus , known as group b strep. The introduction of the protein conjugate vaccines against uenzaehaemophilus infl type b,
A poor prognosis also is associated with reduced cerebral perfusion pressure. Meningitis is an infection (bacterial or viral) of the protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord (meninges). Bacterial meningitis continues to be an important cause of mortality and morbidity in neonates and children throughout the world.
In infants, they might include fever, hypothermia, lethargy, irritability, poor feeding, vomiting, diarrhoea, respiratory distress, seizures, or bulging fontanelles. Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges (the membrane covering the brain and spinal cord). Infants with onset of bacterial meningitis in the first 90 days of life were included in this study.
Bacterial meningitis can also cause death. Bacterial meningitis of infants and the children remain severe as demonstrated by the high rate of mortality in africa [8] [13]. Videos (0) bacterial meningitis is inflammation of the layers of tissue surrounding the brain and spinal cord (meninges) caused by bacteria.
What increases my child�s risk for bacterial meningitis? The spectrum of sonographic features of meningitis included normal scans (30 patients), ventriculomegaly (11 patients), echogenic sulci. Infants may present with nonspecific symptoms and signs (eg, lethargy, irritability, poor feeding, fever or hypothermia).
Videos (0) bacterial meningitis in infants is a serious infection of the meninges and subarachnoid space. This review summarises information on the epidemiology, pathogenesis, new diagnostic methods, empirical antimicrobial regimens, and adjunctive treatment of acute bacterial meningitis in infants and children. The incidence of bacterial meningitis in children differs by age group and is highest in infants aged younger than two months [11,12].
The introduction of the protein conjugate vaccines against haemophilus influenzae type b, streptococcus pneumoniae, and neisseria meningitidis has changed the epidemiology of bacterial meningitis. Reduced cbf is associated with cerebral edema and a poor prognosis. Proven meningitis was defined as the detection of bacteria from cerebrospinal fluid (csf) by culture or molecular techniques during life or at autopsy.
Morbidity among survivors remains high. Treatment of bacterial meningitis requires hospitalization. Bacterial meningitis can be caused by several different types of bacteria.
The diagnosis is based on the results of. The introduction of the protein conjugate vaccines against haemophilus influenzae type b, streptococcus pneumoniae, and neisseria meningitidis has changed the. Meningitis can be very serious if not treated quickly.
Sonograms were obtained during the acute illness and medical records were reviewed. Newborns with bacterial meningitis are usually irritable, vomit, or may have seizures. The course of infection in this group is severe and usually systemic in nature.
If your child is showing signs of. A retrospective study was performed on 78 patients (newborn to 2 years old) with clinically proved bacterial meningitis. Acute bacterial meningitis in infants and children.
Meningitis, pneumonia and sepsis in neonates and young infants (age < 60 days) are leading causes of childhood death in developing countries [1, 2].these conditions have usually been studied collectively as �serious bacterial infections�. Acute bacterial meningitis in infants and children kwang sik kim bacterial meningitis continues to be an important cause of mortality and morbidity in neonates and children throughout the world. Sonograms were obtained during the acute illness and medical records were reviewed.
Suspected meningitis was defined as the detection of a bacteria recognized to cause central. Bacterial meningitis continues to be an important cause of mortality and morbidity in neonates and children throughout the world. To determine the rate of bacterial meningitis among febrile infants in the emergency department (ed) who have pyuria detected in an initial catheterized urine specimen.
Amongst the pediatric population, neonates (up to 4 weeks of age) and infants are particularly susceptible. This retrospective chart review, conducted at the hospital for sick children, toronto, ont., involved all children aged 0 to 3 months who presented to the ed with fever.