The other soft tissue sarcomas of childhood include a wide range of different histologies including fibro sarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, liposarcoma, schwannoma, soft tissue ewing’s / peripheral neuroectodermal. About half of all childhood soft tissue sarcomas are rhabdomyosarcoma, which arises from skeletal muscle, these are most common between the ages of 2 and 6.

The other soft tissue sarcomas of childhood include a wide range of different histologies including fibro sarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, liposarcoma, schwannoma, soft tissue ewing’s / peripheral neuroectodermal.
Childhood soft tissue sarcoma. Having certain diseases and inherited disorders can increase the risk of childhood soft tissue sarcoma. Every life deserves world class care Orthopaedic, cancer and other specialists collaborate to provide your child with individualized care and the best possible outcomes.
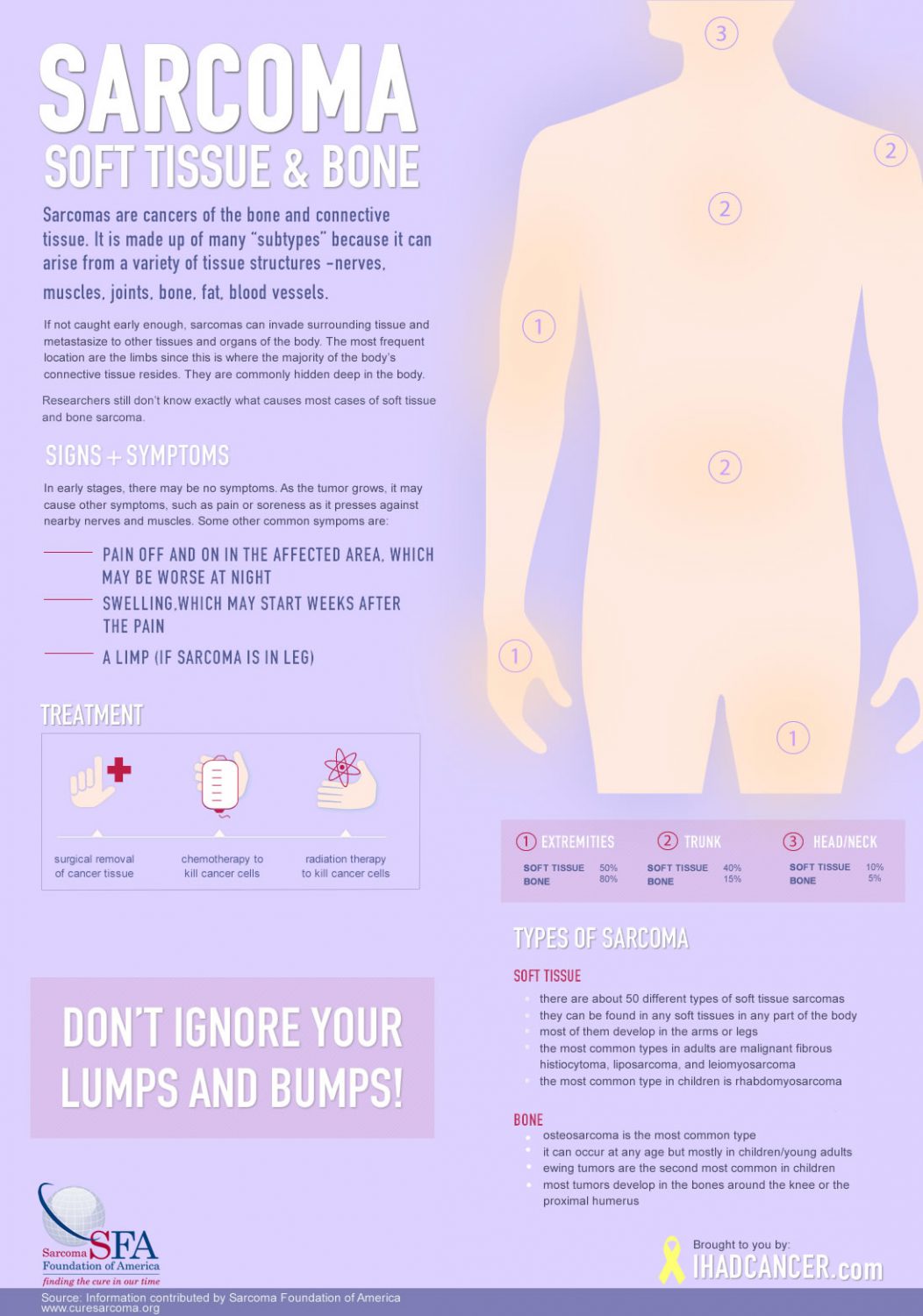
Any such unexplained mass must be diagnosed by biopsy. A soft tissue sarcoma is often a painless mass that grows slowly over months or years. The soft tissue include the following:
Survivors of sarcoma have a significantly increased risk of getting a second cancer. To help understand these differences in outcomes, we discuss the following issues with regard to the management of these patients with soft tissue sarcomas: Treatment for soft tissue sarcomas vary, depending on the size, location, and rate of growth.
Refer to the pdq summary on childhood rhabdomyosarcoma treatmentfor more information.) It’s a rare cancer, and although the cause is not known, you can rely on our pediatric experience to help us identify the cause of your child’s symptoms, and to help you through every step of your child’s medical. Childhood soft tissue sarcoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in soft tissues of the body.
At chop, experts at the bone and soft tissue tumor program at chop take a team approach to treatment. Pediatric soft tissue sarcomas are a heterogenous group of malignant tumors that originate from primitive mesenchymal tissue and account for 7% of all childhood tumors.[ 5] the distribution of soft tissue sarcomas by histology and age, based on the surveillance, epidemiology, and end. A mix of bone and cartilage.
In the united states, doctors diagnose about 900 children and adolescents with soft tissue sarcomas each year. Soft tissue sarcomas can develop in soft tissues like fat, muscle, nerves, fibrous tissues, blood vessels, or deep skin tissues. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers.
Other soft tissue sarcomas, 3%). According to the american cancer society, about 340 children in the nation are diagnosed with rhabdomyosarcoma each year. Rhabdomyosarcoma, a tumor of striated muscle, is the most common soft tissue sarcoma in children aged 0 to 14 years and accounts for 50% of tumors in this age group.[2] (.
Childhood soft tissue sarcoma is a disease in which cancer ( malignant) cells begin growing in soft tissue in the body. The soft tissues include muscles, tendons (bands of fiber that connect muscles to bones), fibrous (connective) tissues, fat, blood vessels, nerves, and synovial tissues (tissues around joints). The outlook for a child with this cancer depends on the type of tumour, where it is, and whether it is slow or fast growing.
A sarcoma is a type of cancer that starts in tissues like bone or muscle. Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most common childhood soft tissue sarcoma. They can be found in any part of the body.
It grows in the muscles attached to the skeleton. A soft tissue sarcoma is a rare form of cancer that grows in the soft tissues of the body. Distribution of soft tissue sarcoma by age and histology.
This pdq cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of childhood soft tissue sarcoma. General information about childhood soft tissue sarcoma. The soft tissue include the following:
Delays in diagnosis, trial availability and participation,. Sarcoma in children tends to grow aggressively and can be difficult to treat. The soft tissues of the body include the muscles, tendons, fat, blood vessels, lymph vessels, nerves, and tissues around joints.
Soft tissue sarcoma (redirected from childhood soft tissue sarcomas ) oncology a sarcoma that arises in muscle, fat, fibrous tissue, blood vessels, or other supporting tissues. Survival rates in children younger than 15 are around 77% for soft tissue sarcoma and 81% for bone tumours. Soft tissue sarcomas are rare, comprising less than 1 percent of all new cancer cases per year and just 3 percent of all childhood tumors.
Childhood soft tissue sarcoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in soft tissues of the body. Pediatric soft tissue sarcomas are a heterogenous group of malignant tumors that originate from primitive mesenchymal tissue and account for 7% of all childhood tumors (rhabdomyosarcomas, 4%; Childhood soft tissue sarcomas (sts) constitute a heterogeneous group of mesenchymal malignancies.
The other soft tissue sarcomas of childhood include a wide range of different histologies including fibrosarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, liposarcoma, schwannoma, soft tissue ewing�s / peripheral neuroectodermal. There are many types of soft tissue sarcoma. The other soft tissue sarcomas of childhood include a wide range of different histologies including fibro sarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, liposarcoma, schwannoma, soft tissue ewing’s / peripheral neuroectodermal.
Childhood soft tissue sarcoma is a disease in which malignant cells form in the soft tissues of the body. About half of all childhood soft tissue sarcomas are rhabdomyosarcoma, which arises from skeletal muscle, these are most common between the ages of 2 and 6. Soft tissue sarcomas can grow anywhere, but they most often grow in the tissue around the arms, legs, shoulders, and stomach.
It makes up 3% of childhood cancers and 2% of adolescent cancers. About half of all childhood soft tissue sarcomas are rhabdomyosarcoma, which arises from skeletal muscle, these are most common between the ages of 2 and 6. Childhood soft tissue sarcoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in soft tissues of the body.
Survival outcomes for adolescent and young adult patients with soft tissue sarcomas lag behind those of children diagnosed with histologically similar tumours. Rhabdomyosarcoma, particularly embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, accounts for the majority of cases. Soft tissue sarcoma occurs in children and adults.
Soft tissues of the body connect, support, and surround other body parts and organs. Doctors are not sure what causes soft tissue sarcomas to emerge, but a genetic link is suspected. There are many types of soft tissue sarcoma.
Soft tissues of the body connect, support, and surround other body parts and organs. Bone and soft tissue sarcomas are the main types of sarcoma. Childhood soft tissue sarcoma treatment (pdq®):
A mix of bone and cartilage. Treatment may include, surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted drug therapy.