It is the most common type of elbow fracture and happens most often to children. In 1958, maylahn and fahey reported that among 300 elbow injuries in children, 6 (2%) were intercondylar fracture of the distal humerus.
As the elbow is forced into hyperextension, the olecranon serves as a fulcrum and focuses the stress on the distal humerus causing fracture.
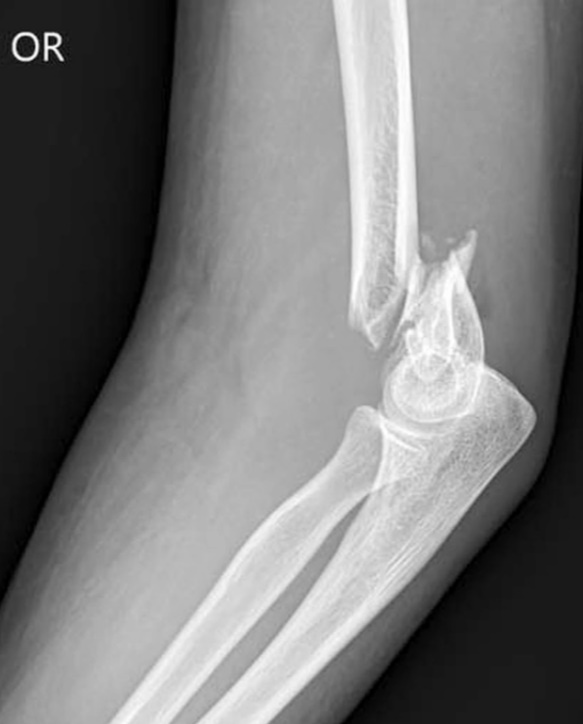
Distal humerus fracture child. This is called a supracondylar (supra con dy ler) humerus fracture. This is the most common type of elbow fracture, and one of the more serious because it can result in nerve injury and impaired circulation. The child’s hand is usually pink.
A fracture of the distal humerus bone ; 10% of all pediatric fractures ; Nonoperative treatment for displaced intercondylar fractures results in complications, including malunion, avascular necrosis, and epiphyseal.
An understanding of the anatomy, biomechanics and growth plate patterns of the distal humerus is vital to the rational consideration of fracture care in children. A displaced supracondylar fracture in a child. In 1958, maylahn and fahey reported that among 300 elbow injuries in children, 6 (2%) were intercondylar fracture of the distal humerus.
Supracondylar fracture (distal humerus) most supracondylar fractures of the distal humerus are as a result of a foosh with the elbow extended. This bone may break (fracture) during sports, a fall, or another injury. They are the most common distal humeral epiphyseal fractures.
Fracture displacement is codified into types, at the distal humerus and the proximal radius. Intercondylar fracture of the distal humerus is an uncommon injury in children. Transphyseal fractures of the distal humerus
Child protection teams evaluated 44 patients (45%) and determined that 24 of those had 25 fractures caused by abuse (25% of the total study population).among children with fractures determined to have been caused by abuse, the. Ipsilateral pediatric elbow and forearm injuries are uncommon, particularly those comprising a supracondylar humerus fracture, radiocapitellar joint dislocation, proximal ulna fracture, and distal forearm fracture. It extends from the shoulder to the elbow, and it is the largest bone in your child�s arm.
The humerus (hu mer us) bone is the long, thick bone in the upper arm that extends from the shoulder to the elbow. At the elbow knob (condylar). The typical mechanism is a fall onto an outstretched hand that puts a hyperextension load on the arm.
As the elbow is forced into hyperextension, the olecranon serves as a fulcrum and focuses the stress on the distal humerus causing fracture. The humerus is a bone in the upper arm. The distal third of the forearm, involving the radius and/or ulna, is the most common location, accounting for about 75 percent of forearm fractures and 20 to 25 percent of all pediatric fractures [ 3,4 ].
Distal humerus epiphyseal separation (transphyseal distal humeral fracture) is rare and has been described only in case reports and small case series. The most common fracture location was the distal humerus (65%) and the most common fracture type was supracondylar (48%). Fractures of the distal humerus belong to the most common injuries of the upper arm in childhood.
In the child, the distal humerus is an osteochondral block, of roughly triangular shape, attached to the distal humeral diaphysis. In this type of fracture, the upper arm bone (humerus) breaks slightly above the elbow. Fractures of lateral condyle of the humerus accounts for 16.9% of all elbow fractures in children and the second most common fracture of the elbow joint after supracondylar fractures.
References this page was last edited on. We present the case of a boy who was 3 years, 6 months old and sustained this constellation of injuries. The distal fragment displaces posteriorly in over 95% of cases.
Fractures of the medial epicondyle ; Anatomy of the distal humerus includes medial and lateral columns. Distal humeral complete physeal separation • often in very young children • may be sign of nat • swollen elbow,“muffled crepitance” on exam • through area of wider cross sectional area than sc humerus fx • restore alignment, may need pinning.
Distal humerus fractures are traumatic injuries to the elbow that comprise of supracondylar fractures, single column fractures, column fractures or coronal shear fractures. The humerus bone is softest at the ends, and most commonly breaks near the shoulder (called a proximal humerus fracture) or near the elbow (called a supracondylar elbow fracture). Diagnosis is made with plain radiographs of the humerus and elbow.
Encompasses several fracture patterns which includes. Common elbow fracture in young children. Kids usually break their arm after falling off the monkeybars or after falling onto an outstretched arm.
Supracondylar fractures (75% of pediatric elbow fractures) 1; These fractures usually occur in children younger than eight years old. It is the most common type of elbow fracture and happens most often to children.
It may happen when your child�s arm or shoulder is hit, or if. Your child’s humerus is fractured (broken) near the elbow area, just above the joint. There is an intervening thin area of bone connecting the olecranon fossa and coronoid fossa, which is the location of most supracondylar humerus fractures.
Forearm fractures are the most common fractures in children, representing 40 to 50 percent of all childhood fractures [ 1,2 ]. Most frequently occurring is the supracondylar fracture of the distal humerus.
