
In children however bones present a greater plasticity and elasticity partly because of a lower Male dominance for distal radius fracture occurred at a comparatively younger age in our population.
This often occurs when a child falls on an outstretched hand that is extended backward.
Distal radius fracture child. [1] most of these fractures are treated conservatively in a plaster and complications are rare. J am acad orthop surg. Noonan is assistant professor of orthopoedic surgery, indiana university, indianapolis.
Distal radius fractures is the most common fracture in childhood. Forearm and distal radius fractures in children kenneth i noonan, md, and charles t price, md dr. Given its contribution to growth there is
The radius and ulna are the two long bones of the forearm, extending from the elbow to the wrist. Complete fractures comprise around 20% of distal metaphyseal radius fractures in children. Distal radius buckle fracture what is a buckle fracture of the distal radius?
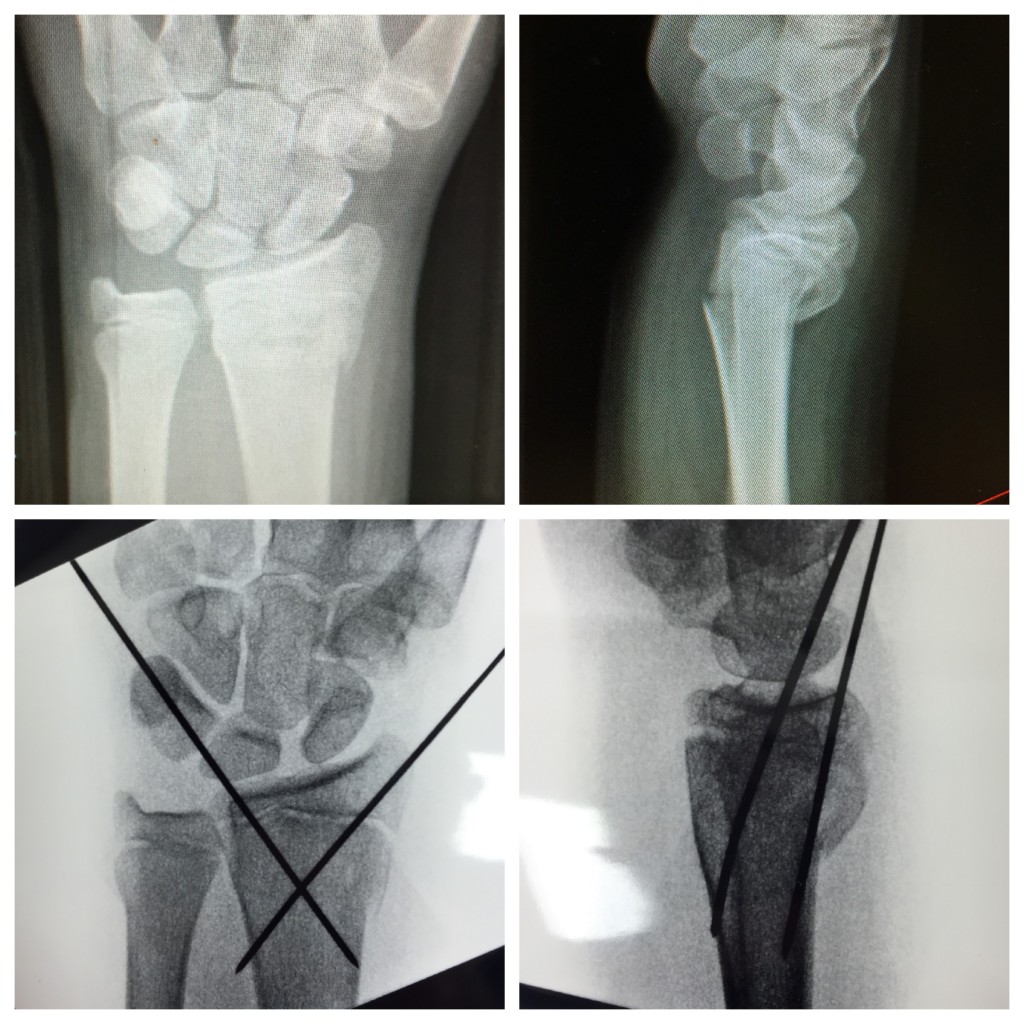
Fall on outstretched hand (foosh) is most common in older population. Buckle fractures of the distal radius are common in children between 2 and 12 years of age buckle (torus) fractures occur when the bony cortex is compressed and bulges, without extension of the fracture into the cortex ( figure 1 ). Abzug jm, little k, kozin sh.
Forearm fractures are common in childhood, accounting for more than 40% of all childhood fractures. Fractures involving the distal radius (dr) of the forearm are common. The radius and the ulna.
• young children with a fracture close to the most active distal physis angulated in the sagittal plane have the highest remodeling capacity. The distal radius accounts for 80% of forearm growth and 40% of upper extremity growth. Fractures involving the distal radius and ulna are commonly seen in children and adolescents.
In children however bones present a greater plasticity and elasticity partly because of a lower Distal radius fractures are common, and are the most common type of fractures that are seen in children. When a child falls on their arm
Price is surgeon in chief, nemours children�s clinic, orlando, fla. Physeal arrest of the distal radius. Metaphyseal and physeal fractures of the distal radius are common in children.
Distal radius fractures represent between 25% and 50% of all broken bones and occur most commonly in young males and older females. The incidence of radial fractures is increasing as life expectancy grows, leading to a larger population of patients who are at risk for these injuries. Distal radial fractures are seen predominantly in children/adolescents and the elderly.
Pin fixation can be used to stabilize the fracture after closed reduction. Metaphyseal and physeal fractures of the distal. Treatment of pediatric distal radius fractures (drfs) is challenging because of possible involvement of the physis and the remodeling capacity by growth.
Price, nemours children�s clinic, 83 w. About three out of four forearm fractures in children occur at the wrist end of the radius. It can also occur along with a fracture of the distal ulna (the forearm bone on the small finger side).
Distal radius fractures • common injury • fractures of the distal radius represent approximately 16% of all fractures treated by orthopaedic surgeons • three main peaks of fracture distribution: Depending on the angle of the distal radius as it breaks, the fracture is called a. Diagnosis is made with radiographs of the wrist.
Distal radius fractures are the most common site of pediatric forearm fractures and generally occur as a result of a fall on an outstretched hand with the wrist extended. Distal radius fractures are a predictor of subsequent fractures. The most common wrist fracture is a distal radius fracture, when the radius (the larger bone in the forearm) is fractured on the distal end, near the wrist.
They usually occur in older children and the thick periosteum helps with reduction and infers inherent stability. Most cases are best treated with closed reduction and cast immobilization. A distal radius fracture can be isolated, which means no other fractures are involved.
Fracture remodelling distal radius fractures in children account for up to 45% of all paediatric fractures. This often occurs when a child falls on an outstretched hand that is extended backward. A buckle fracture can often happen in children because their bones are softer than the bones of an older adolescent or adult.
Dexa scan is recommended for women with distal radius fractures. The most common fracture mechanism is that the child falls on an outstretched arm. Forearm fractures often occur when children are playing on the playground or participating in sports.
In these cases, the injury is called a distal radius and ulna fracture. Distal radius fractures constitute 20 to 35 percent of all childhood fractures. Preventive measures should focus on home environment since this is the most common place for fracture to occur.
It is made up of two bones: Childhood distal radius fractures is low. Higher energy mechanism more common in younger patients.
In addition, children have the capacity to remodel their bones, which influences fracture management. And are the most common children�s fracture seen in emergency departmen ts (ed) (approximately 32 per 1000 patient s seen). There were 49 (38.8%) children with incomplete fractures, and 19 (15.0%) with physeal plate fractures.
Using rigid diagnostic criteria, appropriate diagnosis can be readily made, which will help limit treatment complications and adverse outcomes. Children have unique anatomic structures particular to them. Children are not small adults, and pediatric distal radius fractures cannot always be treated by applying established principles for adult fractures.
Male dominance for distal radius fracture occurred at a comparatively younger age in our population. 5 background development, anatomy and physiology of the juvenile forearm. Columbia street, orlando, fl 32806