
Review of your child’s medical history; Your child’s fatty liver often can be reduced or reversed if it is in the early stages without fibrosis (scarring).
Pediatric nafld is chronic hepatic steatosis in children ages 18 or younger and is the most common cause of liver disease in children 5.
Fatty liver in child. Simple fatty liver typically doesn’t progress to cause permanent liver damage or complications. Autopsy studies suggest that about 1 in 10 children and adolescents have fatty liver, with or without inflammation. Certain conditions also make children more likely to develop fatty liver disease.
Liver biopsy (when doctors use a small needle to test a small piece of your child’s liver) how do doctors treat fatty liver disease? This article will cover tips for parents to help children maintain a healthy weight. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is a condition in which fat builds up in the liver.
Some known causes of acute (sudden) liver failure include: Most children with nafld are in their early adolescent years. This figure is anticipated to increase in conjunction with the global obesity epidemic.
Inflammation in the liver, due to scarring. It is not an independent disease, in many cases it is part of some other pathologic process. There are two types of fatty liver disease:
Childhood fatty liver disease seldom progresses to more serious conditions like nash or liver cirrhosis. Nafld in children and teenagers is considered a complication arising from obesity, the disease still being poorly diagnosed and insufficiently treated, despite an exponential increase of its prevalence. It can lead to scarring, a damage that is similar to the one which is caused by heavy alcohol consumption.
A 2010 study showed that the prevalence of nafld among junior high school students was estimated at approximately 4% in certain areas of japan 6. Fatty liver must be taken seriously as it makes the liver sensitive to other toxic effects. Liver or spleen (a small organ that helps filter blood) that is larger than normal
Review of your child’s medical history; In addition to excess fat, there is inflammation in your liver. Position paper of the espghan hepatology committee.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (nash) is the form of nafld in which a child has hepatitis—inflammation of the liver—and liver cell damage, in addition to fat in the liver. Liver failure can happen to children of any age. Some children do not have any symptoms of fatty liver disease.
Fatty liver disease in children. Why childhood obesity is considered a health problem; Fatty liver disease can also occur in children with healthy body weights but who may have larger waist circumferences than other children of the same weight and height.
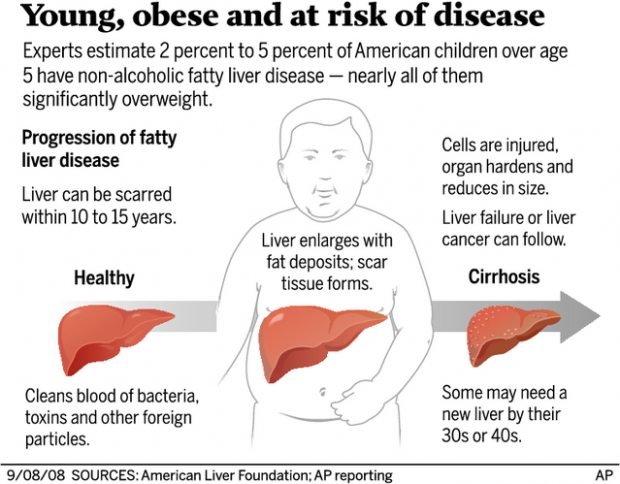
There is less clinical experience regarding nafld/nash in children as. Fatty liver can progress through 4 stages. It is more common in people who:
If kids do have symptoms, which include fatigue, being tired easily or discomfort in the upper right side of. Fatty liver disease can be found in children as young as two years of age. Intensive lifestyle therapy in children and adolescents with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease led to significant weight loss and improvements in liver.
Eating, diet, & nutrition how can a child’s diet help prevent or treat nafld or nash? Obese children are at the greatest risk for developing nafld. Your child’s fatty liver often can be reduced or reversed if it is in the early stages without fibrosis (scarring).
Review of your child’s risk factors for developing the condition; The liver can fail due to many different types of injury or disease. In adults, the disease is a growing reason for liver transplant and, in some instances, liver cancer.
It is important to diagnose fatty liver disease as early as possible. Nowadays, the fatty liver disease is frequently met in obese and insulin resistance children. In the first phase (before the development of fibrosis) it is reversible, when the inducing cause disappears, the liver metabolizes the excessive triglycerides.
Nash is a serious condition that can lead. Call the doctor if your child develops any of these fatty liver symptoms: Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) higher levels of liver enzymes in the blood;
Reduce fatty liver in your child: Alternatively, it could be nash or nafld, where a child’s liver causes inflammation and cell damage. Fatty liver disease can be simple fatty liver disease where a child has accumulated fat in the liver but has no cell damage or inflammation.
Pediatric nafld is chronic hepatic steatosis in children ages 18 or younger and is the most common cause of liver disease in children 5. Fatty liver disease is known as the “silent killer” because it has few or no symptoms at all, even if kids have cirrhosis of the liver. About 1 in 3 australians has fatty liver.
Eating a healthy diet, limiting portion sizes , and maintaining a healthy weight can help prevent nafld and nash in children. Simple fatty liver disease, when a child has accumulated fat in the liver but no inflammation or cell damage. What is fatty liver disease in kids.
Schwimmer jb, deutsch r, kahen t et al. Worryingly, nafld in childhood persisting into adulthood is likely to. Simple fatty liver is the form of nafld in which a child has increased fat in the liver but little or no inflammation or liver cell damage.
Pain in the upper right part of the belly; Diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: Prevalence of fatty liver in children and adolescents.
Typically, there are no visible. Often, a cause cannot even be found. Fatty liver can be caused by drinking too much alcohol over long periods.
Have high cholesterol and high triglycerides. Fatty liver disease is increasingly recognised in children in the absence of identifiable inborn errors of metabolism. Usually the abnormality of liver tests is discovered while investigating for abdominal pain, or liver function tests get reported from an incidental biochemical profile and subsequent ultrasound scan of the liver, suggesting fatty change, and.
Nafld is probably the most common cause of liver disease in children and adolescence [4,5]. Nafld, however, is being increasingly observed in young children. Vajro p, lenta s, socha p, et al.