
Infants identified as at risk of hepatitis b [e.g. Protects other people from the disease because children with hepatitis b usually don’t have symptoms, but they may pass the disease to others without anyone knowing they were infected.
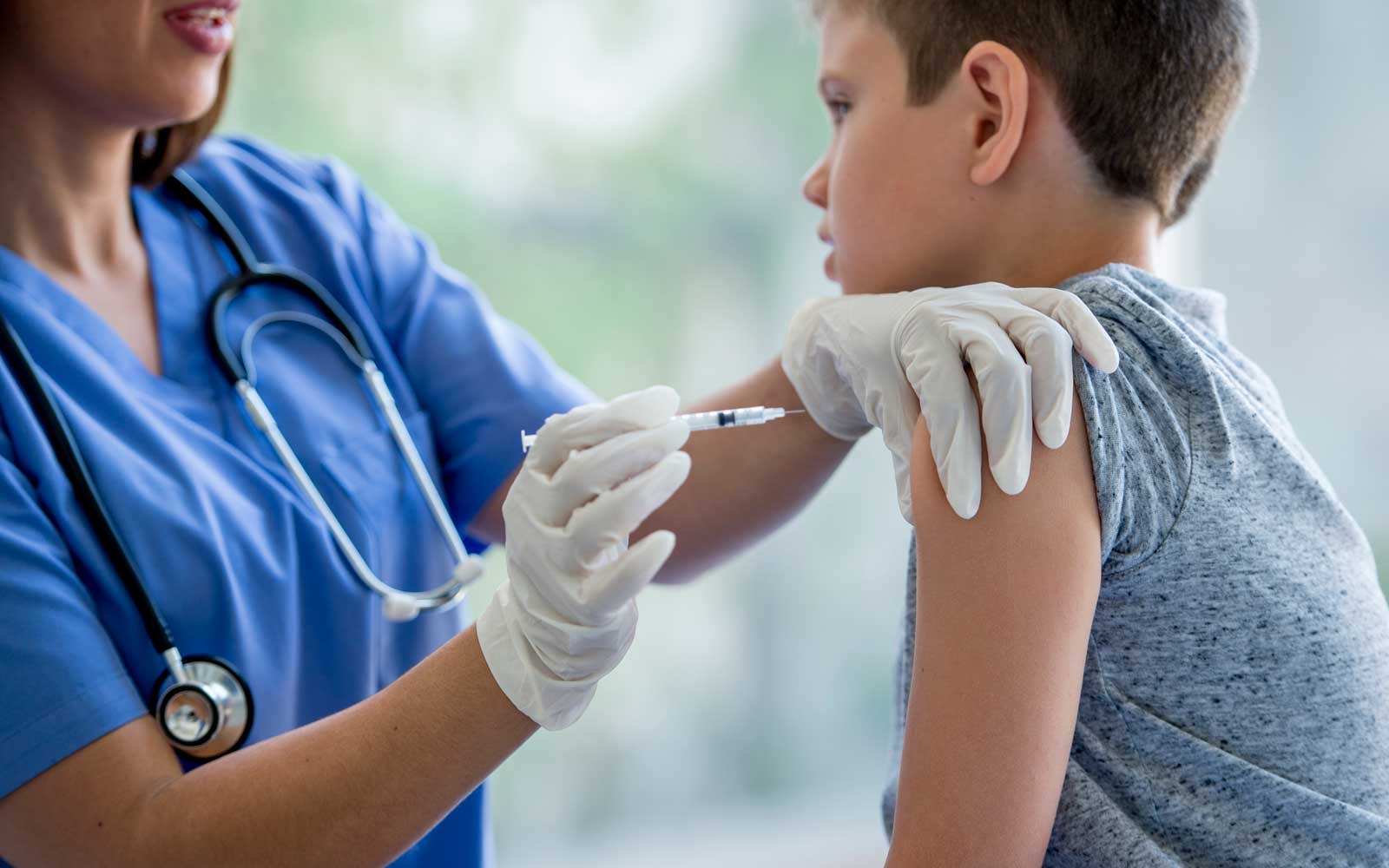
The national immunisation program provides immunisations against hepatitis b for babies from birth.
Hep b vaccine infants. The next 3 doses of hepatitis b containing vaccine are routinely given to. Where can you get a hepatitis b immunisation? If a newborn�s mother carries the hepatitis b virus in her blood, the baby must get the vaccine within 12 hours after birth.
The second dose of single hepatitis b vaccine needs to be given at 4 weeks of age. Hepatitis b virus (hbv) immunization before hbv exposure is the most effective means to prevent hbv transmission. Babies can contract hepatitis b from their infected mother during pregnancy and at the time of birth.
Universal vaccination of all infants at birth. Teenagers not vaccinated as children and all adults at risk of exposure also should be vaccinated against hepatitis b. This vaccine is not recommended in infants weighing less that 2000 g or 4.409 lbs.
• delay first dose of hepatitis b vaccine until chronological age 1 month or hospital discharge, even if the infant weighs less than 2000 g. Babies at risk of developing hepatitis b infection from infected mothers are given extra doses of the hepatitis b vaccine at birth, 4 weeks and 1 year of age. Beginning the hepatitis b vaccine at birth will ensure protection against hepatitis b for life.
It is usually combined with other childhood vaccines such as diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio and haemophilus influenzae type b. Oprophylaxis (hepb vaccine and hbig) for infants born to hepb surface antigen (hbsag) positive women ohbv dna testing for hbsag positive women and antiviral therapy if hbv dna is >200,000 iu/ml. This is if they did not receive the vaccines in childhood.
36 when disease incidence persisted at high rates, the acip altered its strategy again, recommending universal infant vaccination against hepatitis b in 1991. Hepatitis b immunisations are available in each australian state and territory. Babies are routinely given a dose of the hepatitis b vaccine within 24 hours of birth.
Passive antibody from hbig does not interfere with an active response to hepatitis b pediatric vaccine. 2 low birth weight infants (less than 2,000 grams or 4.4 lbs.) should receive 4 doses of hepatitis b vaccine. More countries conduct universal immunization against hepatitis b for neonates and infants.
An effective and safe vaccine is available that reliably prevents hepatitis b. 29 targeted newborn babies, 15 targeted infants and 3. In 2009, 47 member states in the who european region included hepatitis b in their immunization programmes;
Recombivax hb may not prevent hepatitis b infection in individuals who have an unrecognized hepatitis b infection at the time of vaccination. Prophylaxis indications for infants at high risk of hepatitis b. Babies of infected mom’s should be tested at 18 months to be sure baby is hepatitis b free.
(section 5.3) direct quote, “hepatitis b has a long incubation period. Newborns receive the hepatitis b vaccine to prevent them from contracting the hepatitis b virus during their lifetime. Protects other people from the disease because children with hepatitis b usually don’t have symptoms, but they may pass the disease to others without anyone knowing they were infected.
In bc, the hepatitis b vaccine is given to babies as part of their routine immunizations at 2, 4 and 6 months of age. Kids usually get the hepatitis b vaccine (hepb) as a series of 3 shots: The world health organization recommends all infants receive the first dose of the hepatitis b vaccine within 24 hours of birth (often called the “birth dose”) and to complete the vaccine series with additional shots at 1 month and 6 months of age.
The national immunisation program provides immunisations against hepatitis b for babies from birth. Mother is high risk for hepatitis b, but negative (possible window period) or unknown for hbsag] are also given hbig and/or the first dose of hepatitis b vaccine at birth. Vaccination is suggested for most infants and for children aged 10 and younger whose parents are from a place where hepatitis b is common.
A second dose is given at 1 to 2 months. If your baby�s mother has hepatitis b, your baby should get the vaccine within 12 hours of birth. Protects your child from against hepatitis b, a potentially serious disease.
Prevents your child from developing liver disease and cancer from hepatitis b. Please make arrangements with your doctor and the hospital to receive the hbv vaccine for your baby, prior to delivery, so you are sure the vaccine and/or hbig are available at the hospital so prophylaxis can be given within 12 hours of birth. Infants identified as at risk of hepatitis b [e.g.
Hepatitis b immunization in infants, children, and adolescents will be discussed here, focusing on immunization of infants, children, and adolescents (<18 years) in the united states. A third dose is given at 6 to 18 months. Learn more about the benefits of the hepatitis b vaccine here.
The hepatitis b shot is very safe, and is effective at preventing hepatitis b. People under 20 years old, refugees and other humanitarian entrants of any age, can get hepatitis b vaccines for free under the nip. In 1988, the acip recommended that all pregnant women be tested for hepatitis b, and, if positive, their infants vaccinated within 12 h of birth to prevent transmission to the next generation.
This is a guidance document for healthcare professionals (mainly in primary care) on the hepatitis b vaccination schedule and 12 month testing for babies born to hepatitis b infected mothers. Hbig & hepatitis b vaccine within 12 hours of birth, hepatitis b vaccine at 1 month, 2 months and 6 months of age. The baby also needs another shot — hepatitis b immune globulin (hbig) — to provide protection against.