
Occupational exposure for health workers. During pregnancy in women with chronic hcv infection a significant reduction in mean alanine aminotransferase levels has been reported, with a rebound during the postpartum period.
Learning that you have hep c in pregnancy can bring up a lot of questions.
Hep c during pregnancy. Most women become pregnant during the years between 20 and 40, which is also the age group in which the incidence of hepatitis c infection is rising most quickly. If you are pregnant and have hep c, the american college of obstetricians and gynecologists found that there is roughly a 5% chance of transmission from mother to infant. Hepatitis c testing is recommended at least once for all adults.
In few cases exacerbation of chronic hepatitis c has been reported in pregnancy. Occupational exposure for health workers. Hepatitis c should ideally be treated and cured before a person gets pregnant.
Hepatitis c virus can be transmitted to the infant in utero or during the peripartum period, and infection during pregnancy is associated with increased risk of adverse fetal outcomes, including fetal growth restriction and low birthweight. Pregnant women with hep c have a 5.8% chance of transmitting the disease to their newborns. While that is a relatively low percentage, it’s still scary nonetheless, especially when piled onto all the other probabilities of various complications looming over pregnancy.
During pregnancy in women with chronic hcv infection a significant reduction in mean alanine aminotransferase levels has been reported, with a rebound during the postpartum period. Learning that you have hep c in pregnancy can bring up a lot of questions. Hepatitis c screening during pregnancy should be an opportunity to promote a dialogue between pregnant individuals and their.
Read on to learn more about your chances of passing hepatitis c on to your child during. Most mothers have less than a 10% of chance of passing it on, although those with human immunodeficiency virus ( hiv) may be at an increased. Icp causes itching, especially of the palms of the hands, and increased lfts.
When to test a baby for hep c. The status of hep c can change during pregnancy, so your doctor may recommend testing for hep c both before and after pregnancy. And the bottom line is,.
If you’re pregnant and living with hepatitis c, you may be wondering if you will pass it on to your child. Knowing your hep c status gives you and your care team important information to help you and your baby be as safe as possible. Hepatitis c is a virus which infects the liver.
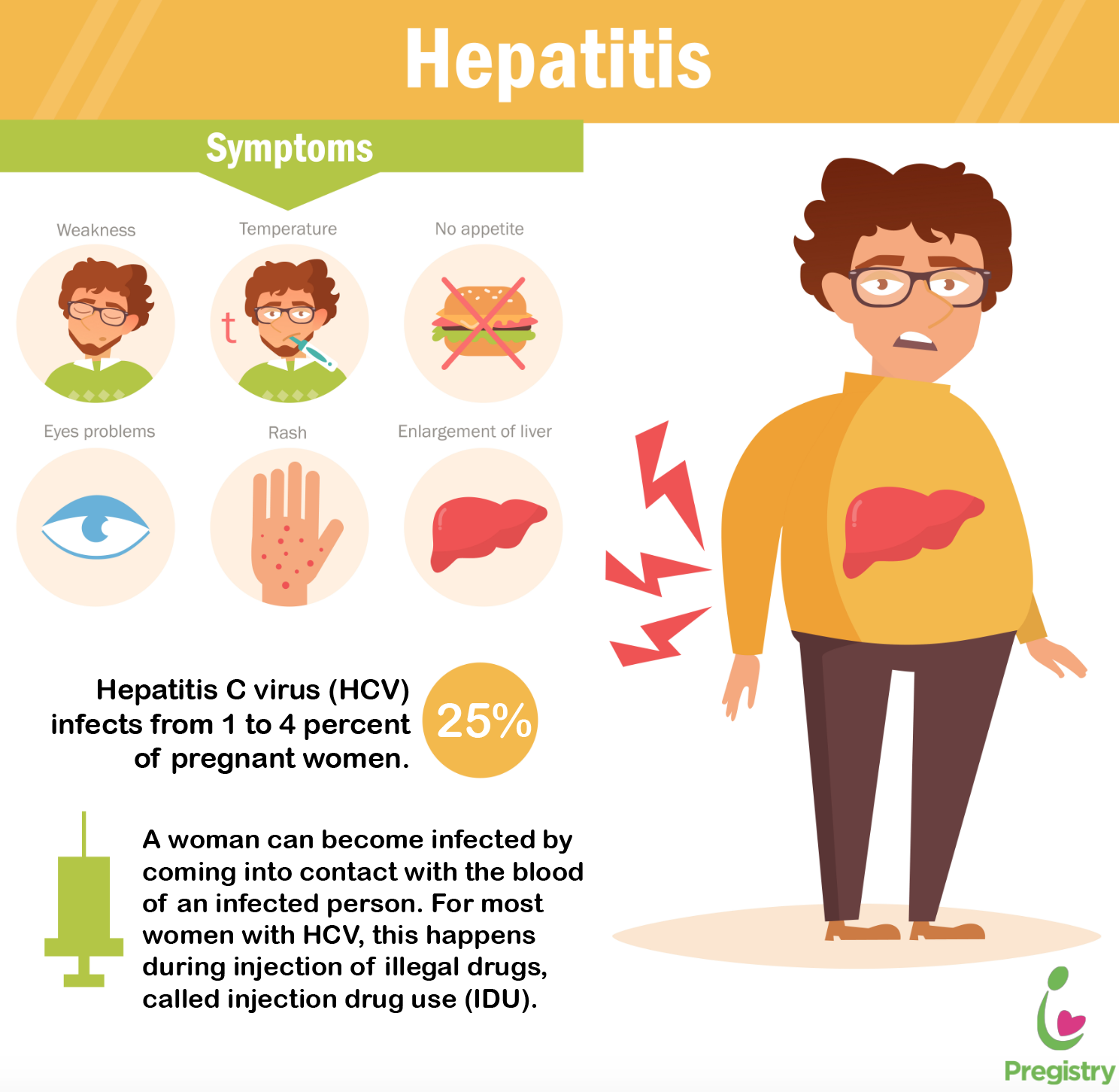
Hepatitis c is a liver infection caused by a virus that is transmitted through contact with the blood of an infected person. Among women already pregnant with hepatitis c, treatment is not recommended during pregnancy, but treatment following pregnancy and. There is an antiviral drug that may be helpful.
According to guidelines from the centers for disease control and prevention, the united states preventive services task force and the american association for the study of liver diseases, all women should be screened for hep c during pregnancy , and infants born to. It is more common if you have hep c. Therefore, treatment during pregnancy is not recommended.
Hepatitis c testing also is recommended for all. Unfortunately, there is not yet good data on whether hepatitis c treatment with direct acting antivirals is safe during pregnancy. Two primary concerns arise from hcv in pregnancy:
Family physicians encounter diagnostic and treatment issues when caring for pregnant women with hepatitis b or c and their newborns. If you test positive for hepatitis c before pregnancy, you can start treatment before getting pregnant. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (icp) is a liver problem of late pregnancy.
Care of women with hepatitis c in pregnancy should be informed by a multidisciplinary team with special expertise in infectious Any woman with risk factors for hepatitis c (such as exposure to transfusions, contaminated needles, or injected drug use) should be screened for hepatitis c before and during pregnancy. About 1 in 20 children born to a mother with chronic hepatitis c become will become infected during pregnancy or delivery.
However, hepatitis c screening has not proven to be cost effective and is not generally recommended [54,55]. This risk is higher for pregnant women who are coinfected with both hep c and hiv —around 10 in 100. Hepatitis b (hbv) like hepatitis c, this virus can cause serious.
Among women already pregnant with hepatitis c, treatment is not recommended during pregnancy, but treatment following pregnancy and completion of breast feeding should be discussed. Research suggests that pregnant women who are infected with hepatitis c have about a six in 100 chance of spreading hep c to their child. Doctors do not generally treat hepatitis c during pregnancy.
If you are a pregnant woman who already has hepatitis c (or gets hepatitis c at some point during the pregnancy), the chance of passing the virus to your baby is low, less than 5 percent. Some will then present with liver damage later in life. Hepatitis c screening during the first prenatal blood assessment obtained in every pregnancy is recommended to identify pregnant individuals with hcv infection and infants who should receive testing at a pediatric visit.
Your baby can be pcr tested at 8 weeks and then 14 weeks old. In the united states, 1% to 2.5% of pregnant women are infected with hepatitis c virus (hcv), which carries an approximately 5% risk of transmission from mother to infant. Your doctor likely won’t treat you for hepatitis c while you’re pregnant because the medications can cause birth defects.
Your baby will only need to be tested for hep c if you had hep c while you were pregnant. The exact chances of spreading it will vary from mother to mother and may depend on how sick the mother is. Other ways of catching the virus include tattooing, body.
Those with hepatitis c during pregnancy are at risk for passing the virus on to their babies. If a mother is infected with hepatitis c during pregnancy, there is a risk that her baby may catch it from her. Hcv can be transmitted to an infant in utero or during the peripartum period.
This will show if your baby has hep c at the time of the tests. Most children infected with this virus will develop chronic infection. If it is severe, it may slightly increase the chance of preterm birth and stillbirth.
The most common scenario is chronic hepatitis c virus (hcv) infection in pregnancy. The risk becomes greater if the mother has both hepatitis c and hiv. In addition, there may be no utility in screening as no.