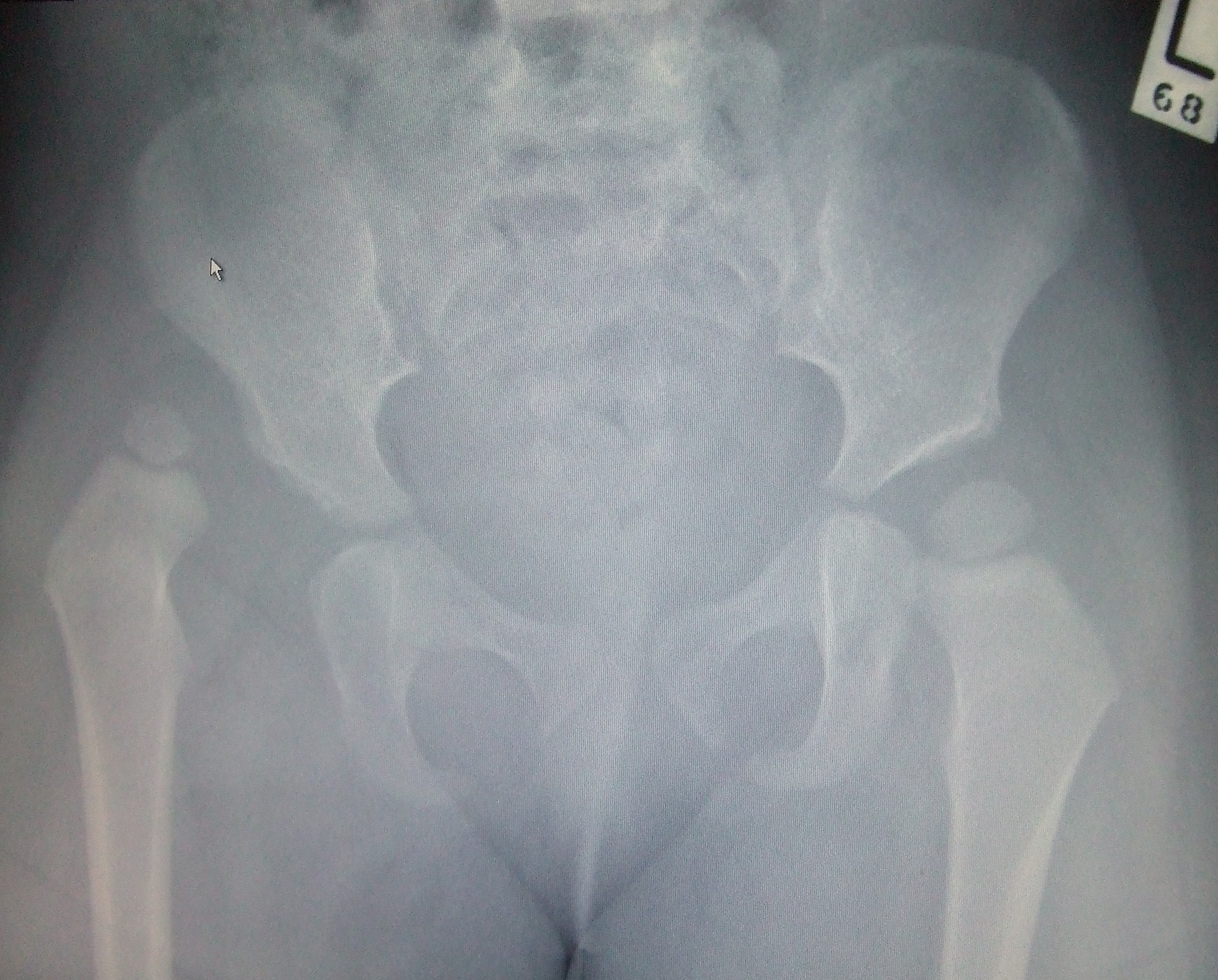
Traumatic hip dislocation is rare in children. The migration percentage (mp) is one criterion used for surgery in dislocated or displaced hips in children with cerebral palsy (cp).
Individuals with hip dislocation may experience:
Hip dislocation in child. When the thigh bone slips out of its socket, it is called a dislocated hip. The most common etiology is spasticity in the context of cerebral palsy (cp); Hip dislocation, neurological hip, paralysis, outcome evaluation, children introduction hip disorders are common in the context of paralysis.
Although ddh is most often present at birth, it may also develop during a child�s first year of life. Children can experience hip dislocations due to congenital conditions, which a doctor will likely detect from routine prenatal screening. Baker, 2011] may be related to increased ligamentous laxity seen in surrounding structures.
Traumatic dislocation of the hip joint in children. Congenital hip dislocation (chd) occurs when a child is born with an unstable hip. Hip dislocation can sometimes occur as a result of hip dysplasia, a developmental condition in which your hip joint doesn’t fit well in the socket.
A hip dislocation is a medical emergency. Traumatic hip dislocation is rare in children. In the mildest cases, doctors will recommend a postural treatment, such as placing the baby in a straddle position.
To restore the stability and. Because the risk of hip dislocation in early childhood is so high, identifying the signs of hip problems as early as possible and appropriately managing them is critical. Developmental dysplasia of the hip (ddh) is a condition where the ball and socket joint of the hip does not properly form in babies and young children.
The migration percentage (mp) is one criterion used for surgery in dislocated or displaced hips in children with cerebral palsy (cp). This may include developmental hip dysplasia, where the. Developmental dysplasia of the hip (dys=bad + plasia=formation) is an abnormal design of the hip at birth (was formerly referred to as congenital hip dysplasia).
Posterior hip dislocation (most common ~85%) anterior hip dislocation (~10%) inferior (obturator) hip dislocation If the child is not carrying weight, the hip cannot develop properly. Transient hip dislocation with spontaneous but incomplete reduction is a diagnostic pitfall that can occur in adolescents.
It�s sometimes called congenital dislocation of the hip, or hip dysplasia. In this condition there is a disruption in the normal relationship between the head of the femur (thigh bone) and the acetabulum (hip socket). And sometimes children who initially seem to have a hip problem actually have underlying pathology of the knee or foot.
In babies and children with developmental dysplasia (dislocation) of the hip (ddh), the hip joint has not formed normally. Your child�s hip is a large and fairly stable joint. Young children in particular may have difficulty localizing or communicating the location of their pain;
Treatments vary depending on the severity of the case and the age of the child. For a child with a right hip dislocation, the pelvis drops on the opposite side (i.e., left), causing instability. The purpose of this study was to investigate the epidemiological features, dislocation types, treatments, and clinical and radiological outcomes.
Hip dislocation in young children can occur with minor trauma; Developmental dysplasia can lead to hip dislocation in infants and children. There are numerous patterns of dislocation 1:
The mp at which a displaced hip can no longer return to normal is unclear. Hip dislocation can occur in children without the presence of a neuromuscular disorder like cerebral palsy, due to conditions like developmental dysplasia of the hip or a sudden injury. Developmental dysplasia of the hip is a common disorder affecting infants and young children.
Dislocation of the hip joint in children 91 most district hospitals in sweden now have an orthopaedic department. It’s caused by abnormal formation of the hip joint during their early stages of fetal development. In adolescents, greater force is required to produce a traumatic complete hip dislocation.
Hip dislocations account for ~5% of all dislocations 3. If the interval from injury to reduction exceeds 3 weeks, we suggest that the surgeon release the adductor longus, lengthen the psoas tendon, and insert a kirschner wire. The hip is a ball and socket joint.
Children with hip pathology may present with hip pain or a limp. A hip dislocation is a very serious injury and should be treated as an emergency, especially in children and teens because their bones are still growing. Muscles that bring legs together into a sitting position are much tighter than the muscles that bring the legs apart and straight at the hips.
Any asymmetric widening of the hip joint warrants additional investigation. Treatment of this condition has previously been described in a dedicated instructional course lecture [1]. The hip joint attaches the thigh bone (femur) to the pelvis.
The ball is loose in the socket and may be easy to dislocate. The slow subluxation and dislocation in children with cerebral palsy is not the same as a sudden painful hip dislocation that can happen after an injury. Only a few are treated by paediatricians,
Usually it takes a serious injury, or trauma, to make the thigh bone slip out of its socket (dislocate). This happens slowly over time. Hip subluxation and dislocation occur when the hip joint is out of position.
Developmental dysplasia of the hip. The pediatric orthopedic team at cook children�s is uniquely trained in the diagnosis and treatment of bone, joint and musculoskeletal injuries. However, treatments for cp patients with hip subluxation and dislocation may differ from treatments recommended for patients who are otherwise healthy.
Another reason may be related to muscle tone and spasticity, or how muscles contract or stay tight. Firth gb, mazibuko ad, munir m. The treatment of congenital hip dislocation.
The differential diagnosis can be narrowed down according to age (see table). Hip dislocation is a relatively rare entity and may be congenital or acquired. This article, as do others, refers to the use of mri and ct scan in investigating young patients with hip dislocations.
The head of the femur (top of the thigh bone) is. All cases of diagnosed or suspected dislocatioin of the hip in the neonatal period are referred to the department of ofiopaedics for investigation and treatment. This might be something like a hard fall, a car crash, or something else of great force.
Children with traumatic hip dislocation should undergo reduction as soon as possible. Individuals with hip dislocation may experience: Before the age of 6 months, it’s not necessary to treat all cases orthopedically.
Hip dysplasia is also called “developmental dislocation of the hip” (ddh).
