With the child lying on his or her side, the hip is passively extended. It is twice as common in boys.

Sometimes, even standing can be too painful.
Hip pain in child. In the meantime, modify your child’s pose. Hip pain in athletes involves a wide differential diagnosis. There may be pain on maneuvering the hip joint.
Antibiotics may be all that’s needed to treat some infections. The child does not usually appear ill, absent or low grade fever, and the esr, crp, and wbc count are normal or slightly elevated. Ernest sink is the chief of the hip preservation service and a pediatric orthopedic surgeon specializing in hip surgery and treatment.
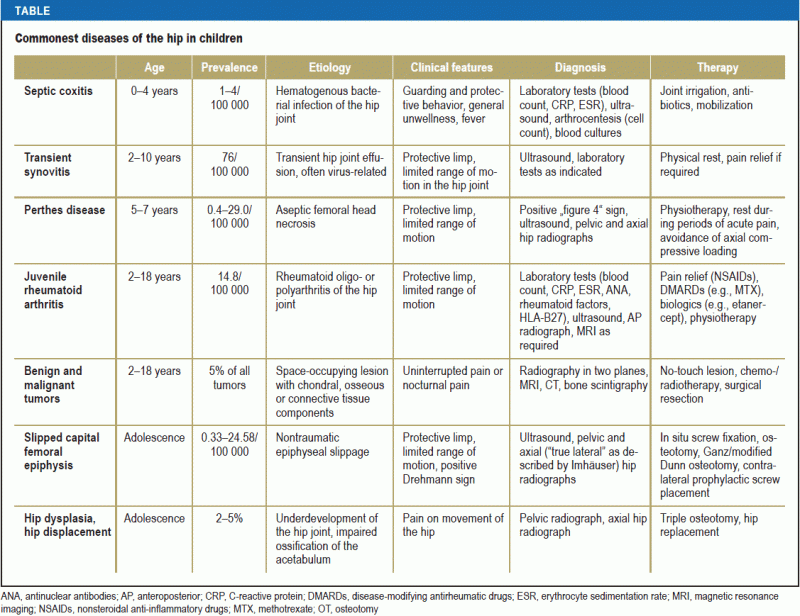
Other bacterial infections or lyme disease (which your child may get from the bite of an infected tick) can also cause hip pain. The difference between growing pains and chronic hip pain. Hip pain is common in children and adolescents and has a broad range of causes, ranging from the benign to the potentially devastating ( table 1) [ 1 ].
Without an adequate blood supply, the “ball” in the socket of the hip becomes inadequate and the bone gradually breaks down. Transient synovitis, one of the most common causes of hip pain in children, must be differentiated from septic arthritis. There are a number of hip disorders affecting children that can cause pain in the hips, groin, thighs, or knees.
A baby in pain may cry, be fussy, and have other signs of pain. Septic hip disease in children refers to an infection in the hip joint which can cause hip pain which often comes on suddenly, a refusal to walk, and often a fever and other symptoms which suggest an infection. Children with hip pathology may present with hip pain or a limp.
Hip dysplasia can remain silent for many years and manifest itself via hip pain during adolescence. Adolescents and young adults are at particular risk for various apophyseal and epiphyseal injuries due to lack of ossification of these cartilaginous growth plates. And sometimes children who initially seem to have a hip problem actually have underlying pathology of the knee or foot.
A child who has a hip problem may feel pain in the hip, groin, thigh, or knee. Pain with hip extension indicates a positive test. Hip pain may be caused by conditions unique to the growing pediatric skeleton including perthes disease, slipped capital femoral epiphysis and apophyseal avulsion fractures of the pelvis.
This pain type can cause a child to limp, as pain increases when they stand or walk. Growing pains usually occur in children under the age of 10 and take the form of pain in the legs, knee and hips at night after a day of activity. With the child lying on his or her side, the examiner passively extends the hip.
If the pain is so severe that a child cannot put any weight on it,. This is a lecture about causes of hip pain in children. Older athletes are more likely to.
Although this is painful, it is. Radiograph is normal or only small effusion present. Hip pain is a common complaint that can be caused by a wide variety of problems.
Symptoms maybe intermittent and occur after activity. Hip pain in children is often accompanied by a protective limp and reduced mobility of the hip. The differential diagnosis can be narrowed down according to age (see table).
It is twice as common in boys. Radiographs of infants and young children with toxic synovitis may show joint space widening on the affected side (. Your child gets sudden pain in their hip, thigh or knee (hip problems can sometimes be felt in the thigh or knee) your child is limping or cannot put any weight on 1 leg.
Toxic synovitis typically produces fewer acute symptoms than does its more serious mimic, septic arthritis. The most common cause of hip pain in older adolescents stems from simple overuse. Symptoms affect both hips in as many as 5 percent of cases.
Children may find it difficult to walk, or walk with a limp. The most common bacterial cause of septic arthritis of the hips in kids is a bacteria called group b streptococcus. If your child is limping or complaining of hip pain, it could be a condition called toxic synovitis that usually isn�t serious.
An irritable hip, or transient synovitis, is associated with restricted movement in a healthy child. If your child experiences pain or difficulty in walking, you should see a pediatric orthopedic specialist. Young children in particular may have difficulty localizing or communicating the location of their pain;
Primary care providers working with kids will likely encounter cases of hip pain in their young patients. This type of pain may indicate an issue with the hip itself; Sometimes, even standing can be too painful.
Some cases are benign, others could be potentially devastating. They may have irritable hip (inflammation of the hip joint). Hip pain / perthes disease.
Hip problems may be present at birth (congenital) or may develop from injury, overuse, inflammation, infection, or tumor growth. Below are answers to common questions parents and patients ask about hip pain, along with. Hip pain is a common childhood and adolescent problem with a broad range of causes.
The bolster should be high enough that your pelvis can rest on it evenly. Typically, pain is felt in the groin, anterior thigh or knee. The psoas sign can signal a psoas abscess or appendicitis.
The evaluation and common causes of hip pain in children are reviewed here. Hip pain (usually minimal) or stiffness also may be reported. Atraumatic hip pain in children is one of the most common symptoms with which pediatricians, orthopedists, and general practitioners are confronted, with an incidence of 148 cases per 100 000 persons per year.
Use a bolster underneath your hips so that you do not have to flex the hips as much. Perthes disease is a condition that affects growing children, and is characterised by a temporary loss of blood supply to the hip. Pain with hip extension suggests a possible psoas abscess or appendicitis.
It will take some practice to get the leg to relax fully, but gradually you should gain some range. It is mainly aimed to primary care physicains (pediatricians, family medicine, and emergency medicine. Child may refuse to stand and limp.
The causes of limp in children, approach to the child with a limp, and. Hip pain can be prevalent in children and teens who were born with a hip condition or disease, or could be the result of an injury at any age. With the child lying on his or her side, the hip is passively extended.
A child in pain may limp or be unable or unwilling to stand, walk, or move the affected leg.