Monogenic autoinflammatory diseases should be considered in those who do not fit the picture of recurrent infections and who do. The recurrent symptoms resolve during the first year of life without any sequelae (fig.
The periodic fever syndromes, also known as.
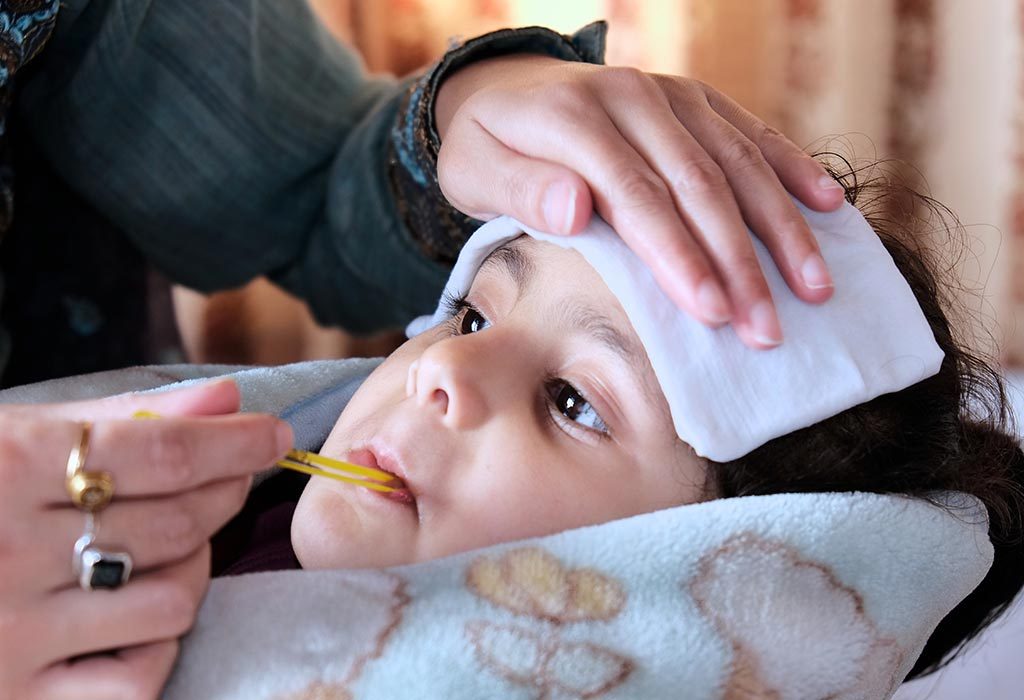
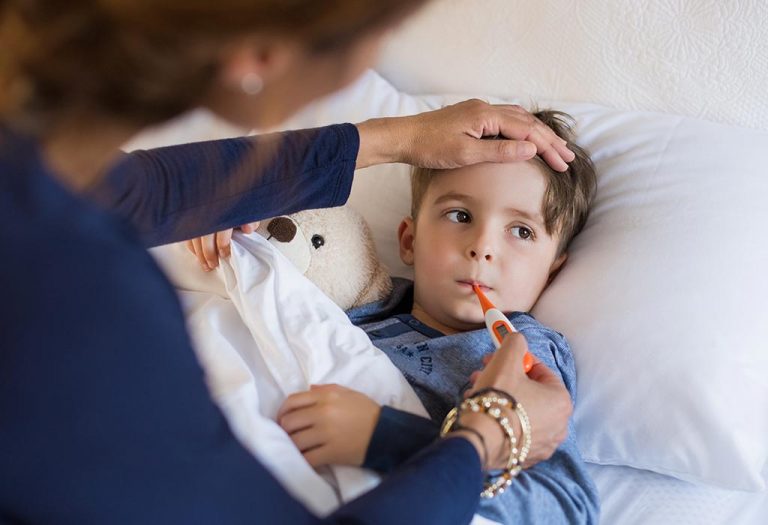
Repeated fevers in children. These are diseases that cause a person — typically a child — to have a fever in a spaced out pattern over time, without having a virus or bacterial infection. Fever in a young baby can be a sign of a dangerous infection. A digital thermometer is preferred as this is an inexpensive, widely available alternative, yielding accurate.
Get medical care right away. The child is healthy and acts normally in between fevers. When an etiology for fever is unidentified on examination, it is termed “fever without source” (fws).
In the young child, recurrent fever episodes are most likely caused by the physiological susceptibility to infections. Some children referred for prolonged fever are actually not having elevated temperatures; Recurrent fevers in children • describe key points on history for a child presenting with recurrent fevers • demonstrate a focused physical exam on a child presenting recurrent fevers • review 3 key rheumatologic diagnoses that include recurrent fever differential diagnosis the top 3 causes of recurrent fever are:
Although repeated febrile episodes are common in young children and often caused by acute viral infections, family members frequently worry about other potential causes such as chronic infections, immune system defects, malignancy, and inflammatory conditions. Periodic fever syndromes and other autoinflammatory diseases are increasingly recognized in children and adults, especially as causes of recurrent fevers. Periodic fever syndromes and other autoinfammatory diseases are increasingly recognized in children and adults, especially as causes of recurrent fevers.
With pfapa, the fever cycle repeats about every three to five weeks. Monogenic autoinflammatory diseases should be considered in those who do not fit the picture of recurrent infections and who do. There is a gap of at least 7 days between two episodes of fever.
Aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis, and adenitis syndrome is the most common periodic fever syndrome in childhood; Children who have this condition may develop a sore throat and mouth sores along with swelling of glands in the neck during a fever episode. Most fevers in young children over 6 months of age are not serious.
However, its underlying genetic basis remains unknown. Recurrent fevers in children are largely due to respiratory viral infections, such as colds and flu, which may cause up to 11 respiratory infections annually and are the leading cause of recurrent fever. You should seek medical advice if the temperature is 39°c or more.
However, recurrent fevers with a repetitive pattern also referred to as periodic fevers are usually of greater concern and require investigation to ensure appropriate diagnosis and management. These episodes can occur at. The periodic fever syndromes, also known as.
Approach to recurrent fevers in childhood. In a 15 minute podcast, dax rumsey (pediatric rheumatologist, stollery children’s hospital edmonton) and his medical student josh koegler outline an approach to recurrent fevers in children, with a focus on rheumatological causes. Although repeated febrile episodes are common in young children and often caused by acute viral infections, family members frequently worry about other potential causes such as chronic infections, immune system defects, malignancy, and inflammatory conditions.
You could measure a child’s temperature by using a glass thermometer or a digital thermometer. This disorder is the most common cause of fever that recurs at regular intervals in children. The approach here requires dissection of the history and correction of health misperceptions.
You should seek medical advice if the temperature is 38°c or more. Monogenic autoinflammatory diseases should be considered in those who do not fit the picture of recurrent infections and who do not have hallmarks of immune deficiency. Your child is 3 months old or younger and has a fever of 100.4°f (38°c) or higher.
Over the centuries the idea. In addition to autoinflammatory diseases, there are some features of recurrent fevers that should warrant a closer look by a child’s pediatrician. Periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis, and adenitis syndrome is the most common periodic fever syndrome in childhood;
However, its underlying genetic basis remains unknown. Febrile episodes in patients with an inherited immunodeficiency usually also manifest. Fevers are said to be recurrent if they occur three or more times within a span of 6 months.
Your child is younger than 2 years of age and a fever of 100.4°f (38°c) continues for more than 1 day. The recurrent symptoms resolve during the first year of life without any sequelae (fig. These include prolonged episodes of fever (more than one week), recurrent fever without symptoms attributable to a viral infection, difficulty growing or gaining weight, or if the child does not return to his baseline.
Your child is of any age and has repeated fevers above 104°f (40°c). Recurrent fevers are common in children. Updated 5/20/19 if you or your child keeps getting fevers, there could be several causes.
These can include periodic fever syndromes, recurrent infection, immunodeficiency syndromes, mast cell activation syndrome (mcas), or autoimmune diseases. Fever in a baby aged less than 3 months is unusual and worrying. Recurrent fevers in children can be diagnosed when the body temperature ranges from as low as 100.4 degrees f to as high as 104 degrees f.
Usually signs of minor infections accompany these episodes; Prolonged and recurrent fevers in children. In a minority of cases, the cause of recurrent fever is a more rare disease that requires second line investigations and specific treatment.
What causes recurrent fevers in toddlers? A fever becomes a matter of concern in children less than 2 years of age or if the fever is persistent. Most children with repeated viral infections as the cause of recurrent fever are seen only
Ultrasonography, ct, and mri can be useful in evaluating the abdomen and can detect abscesses, tumors, and lymphadenopathy. Recurrent fever is one of the main symptoms of a collection of conditions called periodic fever syndromes.