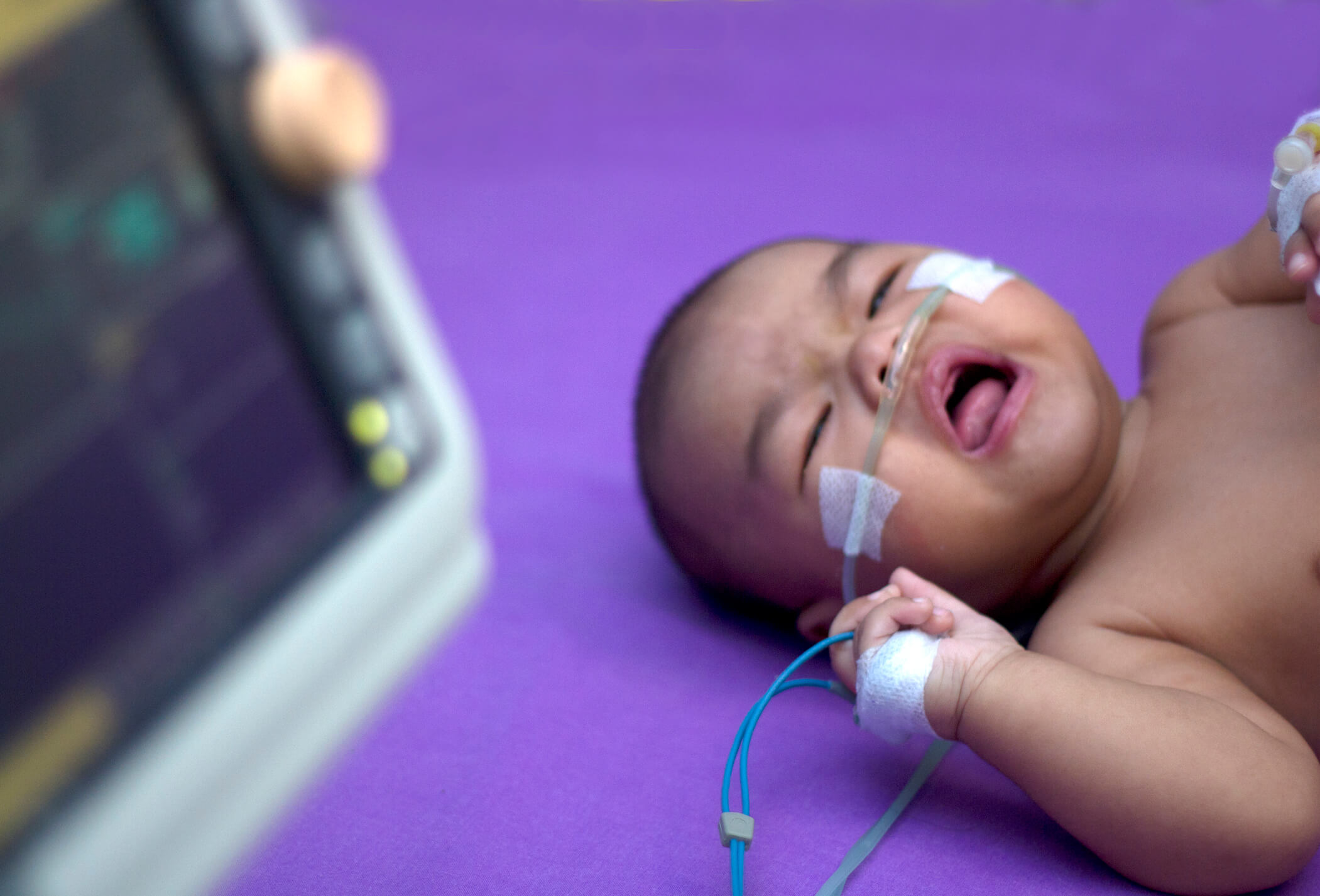
Respiratory distress manifesting as deep breathing or tachypnea is associated with poor outcome in children with severe malaria. Parents can be asked to expose the child.

It is important to learn these signs to know how to respond appropriately.
Respiratory distress in children. As parents, here what you should know and be aware of. Medical advice in a child with moderate respiratory distress or worsening symptoms. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) is a.
The acute respiratory distress syndrome in children: J miss state med assoc. Respiratory distress is often present as respiratory compensation for a profound metabolic acidosis, but can also be.
Low oxygen levels may cause an increase in heart rate. 44 there may be intercostal recession, use of the accessory muscles of respiration and flaring of the alae nasi. Respiratory distress describes symptoms related to breathing problems.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) in children]. There can be many causes of respiratory distress in children. She further tells you that the child�s home ventilator was recently replaced with a newer one.
It is important to learn the signs of respiratory distress to know how to respond appropriately: Children having difficulty breathing often show signs that they are not getting enough oxygen, indicating respiratory distress. This article has examined some of the more common causes of respiratory distress (bronchiolitis, preschool wheeze and asthma) along with rare, but commonly limiting illnesses, such as child.
Respiratory distress syndrome (rds) is a common breathing disorder that affects newborns. The course of illness with respiratory distress syndrome depends on the size and gestational age of the baby, the severity of the disease, the. Respiratory distress is a common reason to alert the paediatric emergency response team or request input from anaesthetists in the hospital setting.
The review intends to provide the physiologic foundation for the treatment strategies that are associated with the most optimal outcome. Less often, rds can affect full term newborns. It can cause babies to need extra oxygen and help breathing.
Three things typically cause respiratory distress in children: This is a list of some of the signs that may indicate that your child is not getting enough oxygen. Respiratory distress syndrome (rds), which used to be called hyaline membrane disease, is one of the most common problems of premature babies.
Chronic illness, infections, or blocked airways. The present review seeks to review the pathophysiologic processes that underlie the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards) in children. Usually it is caused by infections, chronic illness or a blocked airway.
Parents can be asked to expose the child. Since the first description of the “acute respiratory distress syndrome” (ards) by ashbaugh et al in 1967, pediatric intensivists have recognized that ards in children is different from ards in adults.in the absence of identification of these differences, however, children have been characterized as having acute lung injury (ali) and ards based on the adult definitions. Here is a list of some of the signs that could indicate that your child may be in danger of respiratory distress:
An increase in the number of breaths per minute may indicate that a person is having trouble breathing or not getting enough oxygen. The causes include infections, chronic illness or a blocked airway. Respiratory distress describes symptoms related to breathing problems.
Furthermore, what are the signs of respiratory distress in a child? It is important to learn these signs to know how to respond appropriately. Signs of respiratory distress in children.
Rds occurs most often in babies born preterm, affecting nearly all newborns who are born before 28 weeks of pregnancy. The assessment of severity can mostly be made without touching the child. If your child is having difficulty breathing, she may show signs of being in danger of respiratory distress.
When your child can’t get air into their lungs. Acute respiratory distress is one of the most common reason for emergency visits in children under 5 y of age. Respiratory distress frequent reason for call to ems/ed visit due to higher metabolic demands, less reserve, anatomic and physiologic differences, children decompensate more quickly.
In general, children with respiratory distress should have minimal handling. Upon your arrival, the child�s mother tells you that the child was doing fine, but then suddenly began experiencing labored breathing. A child who was premature at birth or has been in the hospital for respiratory problems may be at greater risk.
By learning more about how to treat these breathing issues and how to identify an emergency, you can get your child the care they need in a more timely manner. Respiratory distress manifesting as deep breathing or tachypnea is associated with poor outcome in children with severe malaria. Assessment of the child reveals that she is.
Respiratory distress means difficulty in breathing. An accurate understanding of the epidemiology of these diseases, identification of risk factors and etiology is critical for successful treatment and prevention of related mortality.