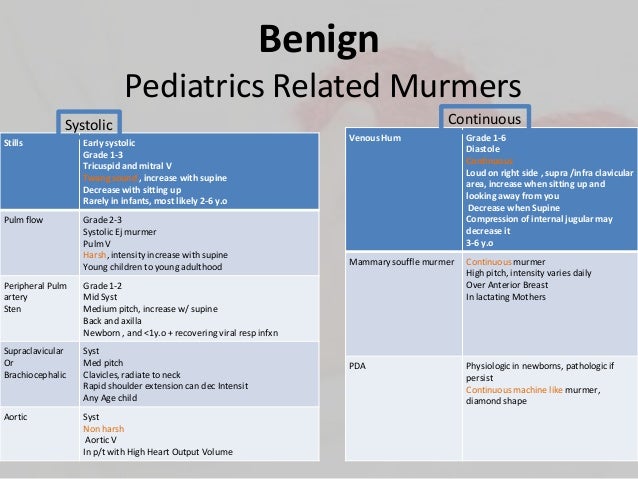
In normal heart murmurs, the flow can be heard pumping through the heart normally. Systolic murmurs are graded by intensity (loudness) from 1 to 6, with a.
In former years the murmur was merely noted.
Systolic heart murmur in child. On a systematic review of cohort studies.) systolic. A heart murmur in children caused by turbulent blood flow can be either normal or abnormal: Its ramifications have been wide and deep.
Congenital heart disease is the. Systolic murmura heart murmur that occurs during a heart muscle contraction. When the rv systolic pressure is elevated, a holosystolic murmur results.
Systolic heart murmurs are heart murmurs heard during systole, i.e. Historical elements that suggest pathology include family history of sudden cardiac death or congenital heart disease, in. Heart murmurs in children are sometimes caused by a structural problem in the heart that the child was born with, such as a small hole between the two lower chambers of the heart, or a �leaky.
Child with a systolic murmurwas investigated with regardtohistory,physicalexamination,fluoroscopic, electrocardiographic andrelatedlaboratoryfindings. Systolic murmurs are divided into ejection murmurs (due to blood flow through a narrowed vessel or irregular valve) and regurgitant murmurs.? A heart murmur that occurs when the heart contracts.
That kind of heart murmur will functional called (or benign) heart murmur. A murmur that occurs when the heart muscle relaxes between beats is called a diastolic murmur. Heart murmurs are extra or abnormal sounds made by turbulent blood flowing through the heart.
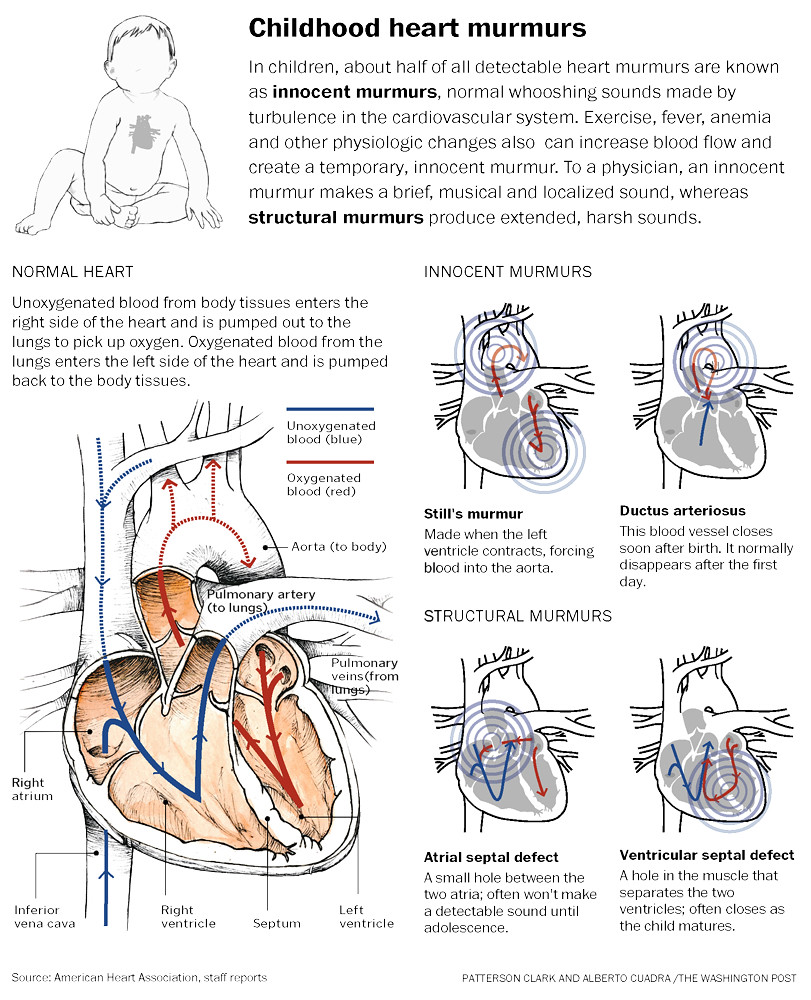
Shortness of breath or breathing fast; About heart murmur in children. Auscultogram from normal and abnormal heart sounds.
7.systolic murmurs 8.diastolic murmurs murmur characterization. A systolic murmur occurs when the heart muscle contracts. Six means a murmur that�s very loud.
Diastolic murmurs are due to a. Systolic murmurs are graded by intensity (loudness) from 1 to 6, with a. In normal heart murmurs, the flow can be heard pumping through the heart normally.
Virtually all children have a heart murmur during their childhood. The murmur is soft, easily heard (but not loud), systolic and heard best at the left sternal edge. Many involve stenosis of the semilunar valves or regurgitation of the atrioventricular valves.
In some cases, the heart murmur can be caused by stress, anemia, or fever. Heart murmur is the most common reason for a referral to a pediatric cardiologist. Although most are not pathologic, a murmur may be the sole manifestation of serious heart disease.
Least common cause of a systolic murmur, occurring in. This extra sound is created by turbulent blood flow. They begin and end between s1 and s2.
Other evidence of cardiac disorder between 6 and 8 weeks of age and at subsequent examinations during childhood. The innocent subclavian murmur (supraclavicular or brachiocephalic systolic murmur) is detected most frequently in children and adolescents. Abnormal heart murmurs in children are generally related to a congenital heart defect;
Children with innocent murmurs have no other symptoms except the abnormal heart sounds. Poor feeding, eating, or weight gain; Some children have very fine chest walls, in which case the heart murmurs can be heard.
In its wake of many curative and palliative procedures for congenital and acquired heart disease, there is a renewed interest in the significance of the cardiac murmur. Similarly, what does a systolic murmur mean? A child with a pathologic heart murmur may have one or more of the following symptoms.
Let’s say that they have an otitis media. An early systolic murmur is a feature of tr with normal rv systolic pressure. Less than 1% of the general population.
Systolic murmurs are divided into ejection murmurs (due to blood flow through a narrowed vessel or irregular valve) and regurgitant murmurs. More than 66 percent of all children, and approximately 75 percent of all newborns, have normal heart murmurs. An organic systolic heart murmur is the result of structural defects in the heart or major vessels.
The development of modern cardiac surgical techniques is one of the great milestones in medicine. Murmurs are graded on a scale of 1 to 6, based on how loud they are. An appropriate history and a properly conducted physical examination can identify children at increased risk for significant heart disease.
Beside above, what does a heart murmur in a child mean? They have a heart rate at the top of the reference range for their age and you hear a murmur. They vary depending on the problem.
Best heard between the third and fourth intercostal spaces of the left sternal edge and the cardiac apex, it. Heart murmurs are common in healthy infants, children, and adolescents. In all cases blood counts were made in order to exclude anaemiaas the cause ofasystolic murmur, andsedimentationrates weredeterminedinasearch for signs of.
In adults they are usually caused by heart valve problems related to age, infection or disease. Evaluation and management of heart murmurs in children. Only the three conditions that cause holosystolic murmurs (vsd, mr, and tr) are the causes of an early systolic murmur.
What are the symptoms of heart murmurs in a child? If a child has a soft systolic murmur at the 6 week check and is growing well and feeding normally with an otherwise normal examination the child can be referred routinely to paediatric outpatients and the parents reassured that the murmur is likely to be due to the normal flow of blood around the heart. In former years the murmur was merely noted.
The parents do not have to worry about this noise. Less than 1% of murmurs are pathological in children. It happens when the blood isn’t flowing smoothly through the heart.
Pathologic causes of systolic murmurs include atrial and. A 3 year old child presents with a febrile illness. This normal blood flow is called an innocent, or normal, murmur.
One means a very faint murmur. A heart murmur is an extra sound heard when a doctor listens with a stethoscope. Serious cardiac pathology may exist without symptoms.
•studies report that as many as 3 in 4 children will have an audible murmur at some point. •as many as 1 in 10 adults will have a. Older children may have a heart murmur.
A systolic murmur is a murmur that begins during or after the first heart sound and ends before or during the second heart sound. Early systolic murmurs may occur in a neonate with a large vsd and in children or adults with a very small. Diastolic murmurs are due to a.