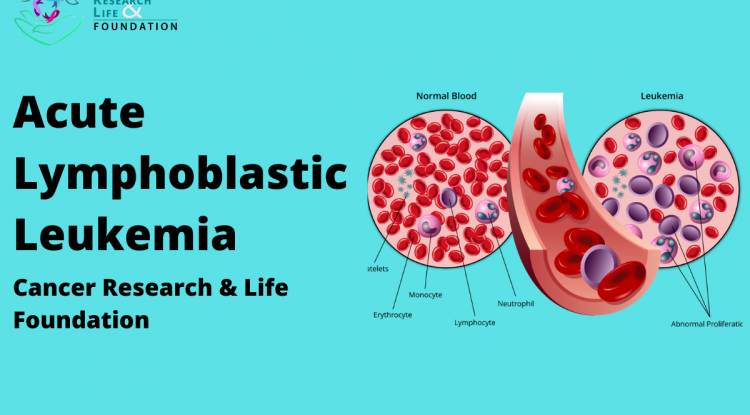
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (lla) is the most common type of leukemia in children. The main treatment for children with acute lymphocytic (lymphoblastic) leukemia (all) is chemotherapy, which is usually given in 3 main phases:

The main treatment for children with acute lymphocytic (lymphoblastic) leukemia (all) is chemotherapy, which is usually given in 3 main phases:
Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood. Pui ch, gaynon ps, boyett jm, et al.: [pubmed abstract] rubnitz je, camitta bm, mahmoud h, et al.: Anthracyclines are used to treat childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (all).
Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the u.s. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (all) is the most common malignant disease in children. Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (all) treatment is usually chemotherapy given in phases and determined by risk group.
Risk classification was based on age, white blood cell count, immunophenotype, genetics (when available), and early response to therapy. Gustafsson g, kreuger a, clausen n, et al. Bm and early relapse (< 30 months from diagnosis.
Deaths and abandonment in first cr occurred in 2.7% and in 7.0% of patients, respectively. Outcome of treatment in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with rearrangements of the 11q23 chromosomal region. Treatment for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (all) depends on your child�s individual situation, including the specific phase of the disease.
Pui ch, yang jj, hunger sp. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (lla) is the most common type of leukemia in children. The main treatment for children with acute lymphocytic (lymphoblastic) leukemia (all) is chemotherapy, which is usually given in 3 main phases:
We conducted a clinical trial comparing the toxicities of two anthracyclines, pirarubicin (thp) and daunorubicin (dnr), in the treatment of childhood all. During induction therapy, 3.0% of patients died, 2.7% abandoned treatment, 1.1% had resistant all, and 93.2% achieved morphological complete remission (cr). Thyroid function following treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia 165 additionally two patients (1 male and 1 female) had compensated hypothyroidism (elevated tsh values with t4 values within the normal range) which resolved spontaneously, as the patients did not receive substitution therapy, and repeat thyroid function tests were normal.
Until now chemotherapy is still used as the main treatment. Jude children�s research hospital (sjcrh) and multiple lics and links fostered by monza�s international school of pediatric hematology‐oncology (mispho) and 14 latin american countries with limited. Nordic society of pediatric haematology and oncology (nopho).
July 1992, teniposide (vumon) was approved for induction therapy in patients with refractory childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia when used in combination with other approved anticancer agents. In addition to systemic control of leukemia, it is crucial for prophylaxis and treatment of sanctuary sites, including the cns. 2 the incidence is about 2 to 5 per 100 000 children.
Radiation therapy, targeted therapy and stem cell transplant are sometimes used. 1 it accounts for one fourth of all childhood cancers and 72% of all cases of childhood leukemia. The nordic experience of 2648 patients diagnosed between 1981 and 1996.
Induction consolidation (also called intensification) Treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia the safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children is a malignant disease or cancer of the blood characterized by the rapid uncontrolled growth of abnormal, immature white blood cells known as lymphoblasts.
Prominent examples include linkages between st. We thought it fitting, therefore, to mark these events by traveling back in time to point out some of the achievements, institutions, study. Bone marrow fibrosis in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia correlates to biological factors, treatment response and outcome.
The relapse rate at a median observation time of 2.1 years was 15.0%. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (all) has been a centerpiece of such twinning relationships; Central nervous system (cns) prophylaxis is typically given to.
Induction — to kill the leukemia cells in the blood and bone marrow and put the disease into remission (a return to normal blood cell counts) Fever, bruising, bleeding, weakness, loss of appetite, and. Even when administered at low doses, these agents are reported to cause progressive cardiac dysfunction.
In some cases, treatment may also include targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and hematopoietic cell transplant (also called bone marrow transplant or stem cell transplant). 3 outcome in all in children has shown a steady improvement. Painless lumps in the neck, groin, or armpits (enlarged lymph nodes ).
Expect your child’s all treatment to include three phases: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is the most common leukemia in children, with approximately 3,000 new patients diagnosed each year in the united states. How is acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated?
The 50 th anniversary of seminars in hematology coincides with the 50th of st. The peak incidence of all occurs between 2 and 5 years of age. Treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and/or stem cell transplant.
A pediatric oncology group study j clin oncol , 10 ( 1992 ) , pp. Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia incidence, survival & related chronic disease. Methotrexate (mtx) is an essential drug in the treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (all).
Treatment regimens for acute lymphoblastic leukemia include central nervous system (cns) prophylaxis to prevent leukemia cells from spreading to the area around the brain and spinal cord. Jude children’s research hospital, and both milestones are inexorably linked to studies contributing to the cure of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (all). As such, the survivor population throughout the developed nations is growing substantially.
Survival of relapsed patients can be predicted by site of relapse, length of first complete remission, and immunophenotype of relapsed all.