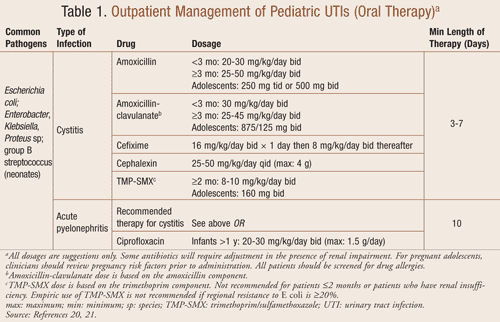
If your child has a uti that’s diagnosed as a simple bladder infection, it’s likely that treatment will consist of oral antibiotics at home. Urinary tract infection (uti) is common in children, and girls are at a significantly higher risk, as compared to boys, except in early infancy.
Most cases are caused by escherichia coli.
Uti treatment in children. Oral antibiotics are appropriate for most children with uti. Oral antibiotic therapy for 7 to 10 days is adequate for uncomplicated. But kids can get urinary tract infections (utis), too.
Urinary tract infection (uti) is common in children, and girls are at a significantly higher risk, as compared to boys, except in early infancy. For enterococci and patients allergic to cephalosporins. Urinary tract infection (uti) is one of the most common bacterial infections of childhood.
Treatment of urinary tract infection is aimed at eliminating the acute infection, preventing urosepsis, and preserving renal parenchymal function. Next, findings from uti studies in children from developing countries will be presented. Bacteria normally found in the bowel cause most utis in children.
1 2 prevalence varies with age, peaking in young infants, toddlers and older adolescents. Collection of an uncontaminated urine specimen is essential for accurate diagnosis. Nearly anyone who has ever suffered from a uti knows that the best cure is cranberry juice.
Used with gentamicin in neonates < 2 wk of age; A uti is when bacteria gets into your urine and travels up to your bladder. Iv medicines are given through a vein.
Most cases are caused by escherichia coli. To provide an update on the evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of urinary tract infection in children. Most urinary tract infections (utis) in children can be effectively treated with antibiotic medication.
Most cases are caused by escherichia coli collection of an uncontaminated urine specimen is essential for accurate diagnosis. For children 3 months or older with acute pyelonephritis/upper uti: A heating pad or medicines to relieve pain;
Up to 8% of girls and 2% of boys. How is a uti treated in a child? Urinary tract infections (utis) are common in childhood.
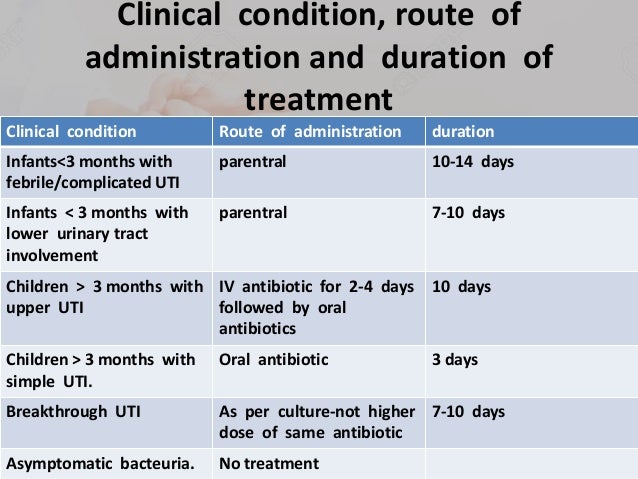
Children who are seriously unwell and most infants under 3 months usually require iv antibiotics Treating urinary tract infections in children. Which antibiotic your child takes is based on age, any allergies to antibiotics, and the type of bacteria causing the uti.
If your child has a uti that’s diagnosed as a simple bladder infection, it’s likely that treatment will consist of oral antibiotics at home. Uti is more common in. Antibiotic treatment guidelines for urinary tract infections in children (60 days through 17 years) this guideline provides guidance for most children 60 days through 17 years of age.
The “urinary tract” is the organs in your body that make. A pubmed search was completed in clinical queries using. What’s the treatment for utis in children?
Kids catch lots of bugs in their first few years of life. Children with acute pyelonephritis can be treated effectively with oral antibiotics (e.g., amoxicillin/clavulanate, cefixime, ceftibuten [cedax]) for. Your child may go to a hospital for intravenous (iv) antibiotics if the child is younger than 2 months old or vomiting.
Treatment will depend on your child’s symptoms, age, and general health. See guidance on dosing in children for quick reference dosage/weight guide. Bladder infections are the most common type of urinary tract infection (uti), but any part of your child’s urinary tract can become infected including the urethra, bladder, ureters, or kidneys.
Safe to use in infants < 6 wk of age; Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are very important to reduce the morbidity associated with this condition. Renal and bladder ultrasonography should be considered in children < 2 years of age with a febrile uti, children of any age with recurrent uti, and children with palpable abdominal mass, abnormal voiding, hypertension, hematuria, no response to standard antimicrobial treatment, and family history of renal or urological disease [9, 41, 70].
Utis are common, especially among girls. Very young infants, those presenting with a toxic appearance, severe dehydration, vomiting, or intolerance to oral medication should be considered for. Diagnosis, treatment, prognosis and prevention of uti in children.
Hospitalization for administration of iv antibiotic therapy may be indicated for children with a suspected uti depending on the severity of their symptoms (table 2). Initially this review will summarize relevant uti literature from developed countries as in comparison fewer studies have assessed its importance in developing countries. Treating a urinary tract infection requires antibiotics that can either be delivered intravenously (through a needle into your child’s veins) or orally (they swallow the pills or liquid).
However, more severe infections may require. As many as 8 in 100 of girls and 2 in 100 of boys will get utis. This medication can often be given at home, although there are some situations where it may be necessary for your child to stay in hospital for a few days.
100 mg/kg/day iv/im divided q8h. Children older than 2 months usually take an antibiotic by mouth—as a liquid or as a chewable tablet. 3 treatment of uti in children sometimes, the clinical presentation and/or urinalysis clearly suggest an uncomplicated uti and the desire is to start treatment empirically.
Urinary tract infection (uti) is common in children, and girls are at a significantly higher risk, as compared to boys, except in early infancy. Young children have a greater risk of kidney damage linked to uti than older children or adults. If uti is suspected in children aged under 3 months — refer urgently to a paediatric specialist for treatment with parenteral antibiotics, and send a urine sample for urgent microscopy and culture.
Colds and other respiratory infections are common. Urinary tract infection (uti) is a common infection in children. Their healthcare provider may also prescribe medications for their fever and/or pain.
It will also depend on how severe the condition is. Management of urinary tract infections (uti) in infants <60 days, pregnant patients, or in patients with recurrent utis is beyond the scope of these guidelines.