
During pregnancy, it is necessary to urinate frequently to prevent the growth of the bacteria in the bladder. The choice of antibiotic should address the most common infecting organisms (i.e., gramnegative gastrointestinal organisms).
Nitrofurantoin (if estimated glomerular filtration rate [egfr] is 45 ml/minute.
Uti when pregnant treatment. Urinary tract infections are most commonly treated by antibiotics. Women with gs urinary tract infection during pregnancy should also receive appropriate treatment at the time of diagnosis as well as iv pregnancy. Complications from a uti or its treatment are rare, but some risks are particular to pregnant people and their babies.
After a health care provider determines the cause of your symptoms, they can propose the appropriate treatment for uti in pregnancy. But if left untreated, they can lead to kidney infections and. It is possible that the uti may take care of itself.
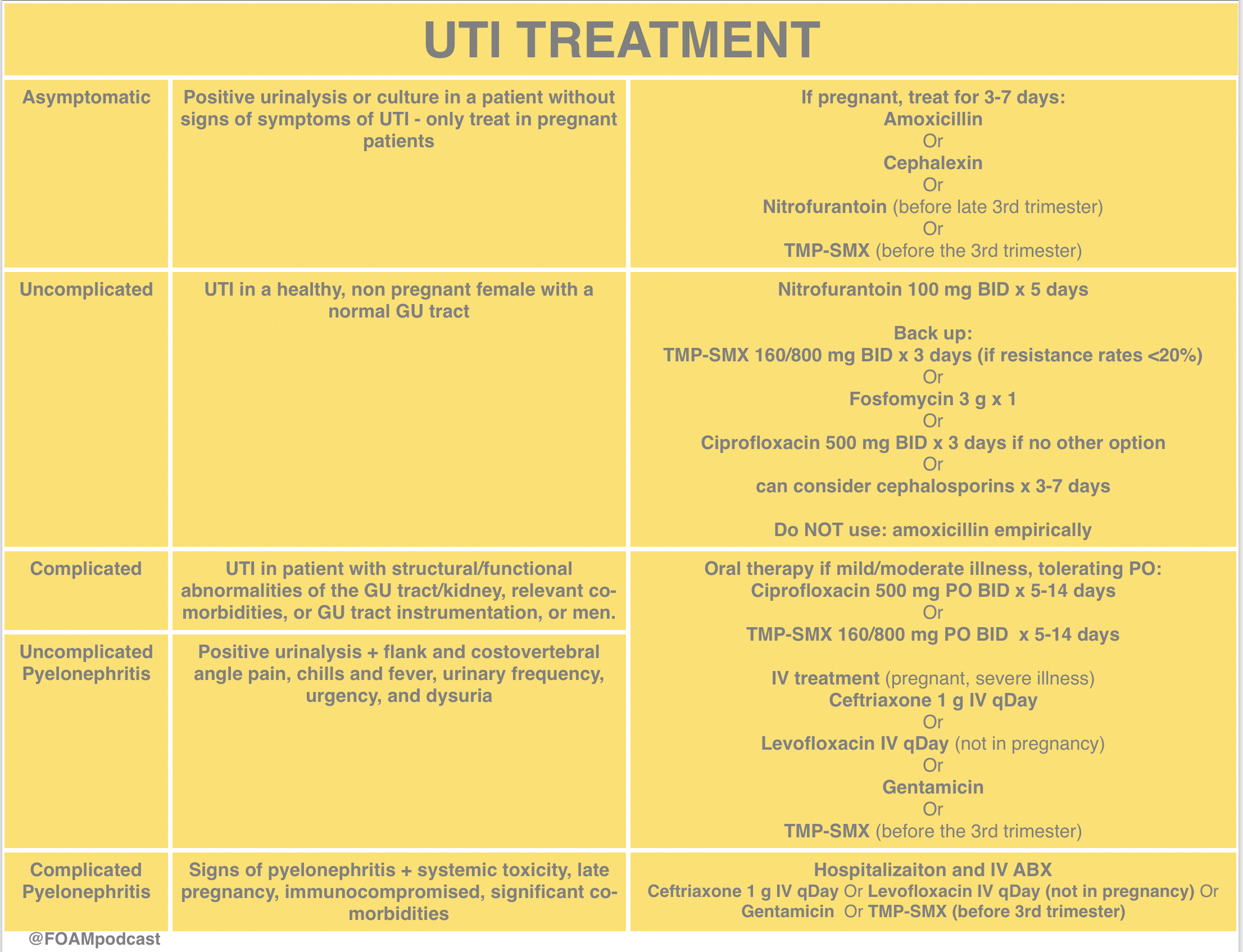
Treatment pregnant women should be treated when bacteriuria is identified (table 217,18). All women should be screened for asymptomatic bacteriuria at the first antenatal visit. Guidance is in agreement that pregnant women with uti be offered an immediate antibiotic to prevent complications such as pyelonephritis.
What are the home remedies to treat uti during pregnancy? Leansing with water and holding the labia apart are not essential. The choice of antibiotic should address the most common infecting organisms (i.e., gramnegative gastrointestinal organisms).
Those who develop one have a 1 in 3 chance of an encore later. Utis can be safely treated with antibiotics during pregnancy. Enter this list of uti pregnancy natural treatment.
Most urinary tract infections, especially the lower urinary tract infection often subside on their own. Despite the body’s natural defences, certain fungi, bacteria, and viruses enter the urinary tract and inhabit the bladder, urethra, and the urinary tract. They are typically prescribed for three to 10 days, depending on the type of.
A uti may manifest as asymptomatic. Every woman has a 20% risk of experiencing a uti in her lifetime. However, pregnancy is a condition that warrants immediate attention if you are suspecting a urinary tract infection.
Infection ascends from the urethra to the bladder. A study from the centers for disease control and. Nitrofurantoin (if estimated glomerular filtration rate [egfr] is 45 ml/minute.
If you continue to have utis after we treat the first one, we may recommend suppressive therapy. Urinary tract infections (utis) occur commonly during pregnancy. The american college of obstetricians and gynecologists (acog) recommends avoiding these antibiotic treatments in early pregnancy if possible.
Unfortunately, there are no natural treatments for utis during pregnancy. Fortunately, utis in pregnancy are most often easily treated with excellent outcomes. Can ascend further to the ureters and the renal pelvises (see “ pyelonephritis ”) causative organisms
Use of antiseptics for cleaning the perineum is not Which antibiotic is safe for uti during pregnancy? If needed, you can address these with your doctor:
Urine samples should be sent for culture and empiric treatment given while awaiting results. The antibiotic should also be safe for the mother and fetus. Pregnant women should be screened and treated both for utis and for asymptomatic bacteriuria.
If there are symptoms of pyelonephritis (such as fever) or a complicated urinary tract infection (uti), see the nice guideline on acute pyelonephritis for antibiotic choices. At least 5 percent of women can expect to develop at least one uti during pregnancy; Medications for the treatment of urinary tract infection during pregnancy antibiotic medications are frequently used to treat urinary tract infections in women who are pregnant.
Nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim or cephalexin are appropriate antibiotic choices (although restrictions apply. However, you can prevent utis naturally or. >105 colonies of a single pathogen/ml clean catch urine.
These antibiotics are mainly antimicrobials from two specific groups — penicillins and macrolides. Most patients receive antibiotics during pregnancy for uti. Antibiotic, dosage and course length.
Do not hold the urine for a long time, the bacteria can overgrow in the bladder. Here are some home remedies that may help recover from uti during pregnancy : With appropriate screening and treatment, this morbidity can be limited.
Uti may present as asymptomatic bacteriuria, acute cystitis (bladder infection) or pyelonephritis (kidney infection). Asymptomatic bacteriuria, acute cystitis, acute pyelonephritis diagnosis for asymptomatic bacteriuria and lower uti: Utis during pregnancy are a common cause of serious maternal and perinatal morbidity;
For the management of upper utis, see “pyelonephritis.” etiology pathogens bacteria. Oral nitrofurantoin and cephalexin are good antibiotic choices for treatment in pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria and acute cystitis, but parenteral antibiotic. Of women experiencing a symptomatic uti during pregnancy.
Natural remedies for a uti during pregnancy. Some of the safe antibiotics used for the treatment of uti during pregnancy are. Your healthcare provider will probably prescribe antibiotics that are safe to take during pregnancy.
Treatment of uncomplicated uti in pregnancy. Most utis during pregnancy are treated with a course of antibiotics. When treated quickly and correctly, utis rarely lead to serious complications;
The recommendations on treatment of uncomplicated uti in pregnancy are based on clinical guidelines from phe , eau and nice [nice, 2018d]. Urinary tract infection (uti) in pregnancy: If you urinate frequently, then it helps you to clear the bacteria from the urinary bladder.
During pregnancy, it is necessary to urinate frequently to prevent the growth of the bacteria in the bladder. Rarely, pregnancies complicated by pyelonephritis will lead to significant maternal and fetal morbidity. Treat women with a positive urine culture for bacteriuria detected during
Changes of the urinary tract and immunologic changes of pregnancy predispose women to urinary tract infection. Treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant patients is important because of the increased risk of urinary tract infection (uti) and its associated sequelae, including increased risk of pyelnonephritis, preterm delivery, and low birth weight.