
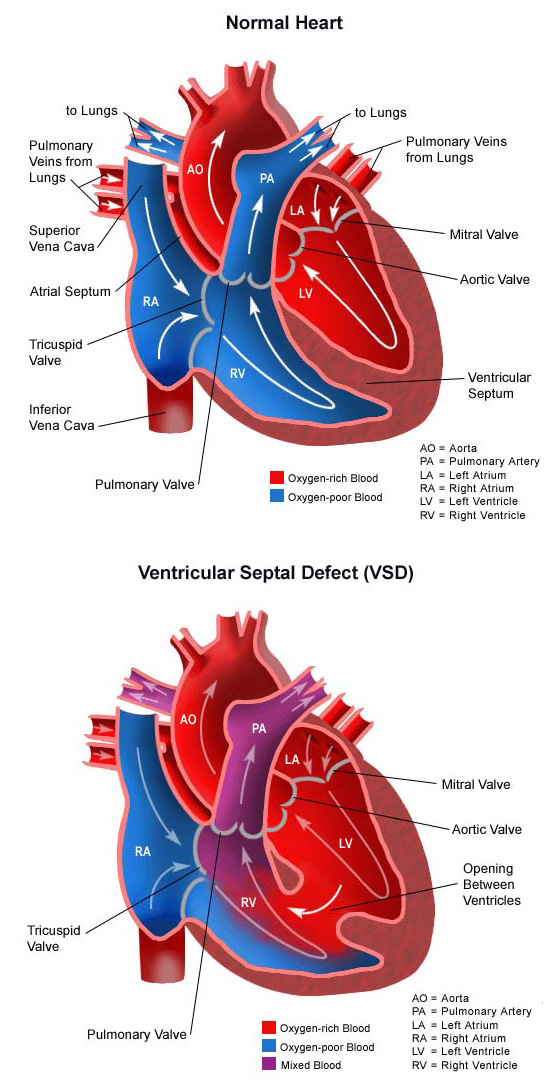
A ventricular septal defect (vsd) is a congenital heart defect. The defect can be small or large.
These chambers are divided by a wall of muscle called a septum.
Ventricular septal defect in infants. Small vsds don�t cause problems and often close on their own. This involves the use of medications to decrease the work of the heart and increase the strength of the heart beat. Ventricular septal defect(vsd) is a type of congenital heart defect resulting in a hole in the muscular wall(septum) separating the two lower chambers of the heart.
Congenital heart defects treatment shows progressive reduction in morbidity and mortality, however, the scar, resulting from ventricular (vsd) and atrial septal defect (asd) repair, may cause discomfort. Usually, ventricular septal defects diagnosed in infancy get smaller with time and even large defects can close completely. Ventricular septal defect (vsd) is one of the most common congenital heart lesions (second only to bicuspid aortic valve).
This means that your baby is born with it. Ventricular septal defect (vsd) is a condition whereby there is a hole between the two pumping chambers of the heart. Ventricular septal defect (vsd) is the most common congenital cardiac anomaly in children and is the second most common congenital abnormality in adults, second only to a bicuspid aortic valve.
The anatomy, pathophysiology, natural history, clinical features, and evaluation of isolated vsds in children will be presented here. A vsd is a hole in the wall between two of the heart chambers that normally isn�t there. The condition is caused by embryologic malformations of the ventricular septum, and can occur as an isolated lesion or in combination with other similar birth defects.
Ventricular septal defect (vsd) is one of the most frequent congenital heart malformations, accounting for 40% of all congenital heart diseases. First, infants may have ongoing symptoms of congestive heart failure. Unrepaired large ventricular septal defects and some moderate ventricular septal defects can cause two problems.
Ventricular septal defect (vsd) is one of the most common congenital heart defects, occurring in almost 50 percent of all patients with congenital heart disease (chd). It is one of the most common types of congenital heart defects, accounting for about half of congenital heart disease cases in babies. A ventricular septal defect (vsd) is a congenital heart defect.
Right axillary minithoracotomy approach, by avoiding the breast growth region, is an option for correction of these defects that may provide better aesthetic results at. Septal defects are sometimes called a hole in the heart. A ventricular septal defect (vsd) is a defect in the septum between the right and left ventricle.
Ventricular septal defect is one of the most common congenital defects that affect newborns. The echocardiographic evaluation and management are discussed separately. Infants with vsd, suffering from intractable heart failure or failure to thrive, require operation in order to survive.
A ventricular septal defect (sometimes referred to as ventral septal defect) is a hole in the ventricular septum that allows communication of blood between the left and right ventricles. These chambers are divided by a wall of muscle called a septum. Vsds can be small or large.
Unless it is severe, many infants with a. A vsd is an opening or hole in the dividing wall (septum) between the 2 lower chambers of the heart (right and left ventricles). 3) they can be isolated, or be an intrinsic component of other simple or complex cardiac abnormalities.
In mild cases the only symptom may be a heart murmur. Ventricular septal defects are the most common congenital heart defect in newborn babies. 1,2) among these, perimembranous vsd is the commonest hemodynamically significant one.
Vsds are the most common type of congenital heart defect. In ventricular septum defect, there is a hole in the septum partitioning the ventricles. A normal heart has four chambers:
In infants with vsd combined with mr, simultaneous mvr has no benefits simultaneous mvr provided no advantage over that of isolated vsd closure. In more severe cases, infants or children may have poor growth, breathing problems, and difficulty eating or sweating. This allows blood to flow from the left ventricle to the right ventricle, which can result in more blood than usual going to the lungs.
Infants who have poor growth due to congestive heart failure can have poor brain development during the first few years of life. Ventricular septal defect (vsd) as an isolated lesion or in combination with other cardiac anomalies is the most common form of chd. It�s less common in older children and adults because some.
Ventricular septal defect (vsd) is an abnormal opening in the ventricular septum, the tissue or wall that separates the heart’s lower chambers (ventricles). It�s the most common congenital heart defect in the newborn; Our cardiorespiratory unit regularly refers to information published by the british heart foundation (bhf) and the children�s heart federation when explaining ventricular septal defect (vsd) to.
If the child develops congestive heart failure, treatment is needed. It is caused by a developmental abnormality that causes the septum to not fully form. 2 atria and 2 ventricles.
The septum is a wall that separates the heart�s left and right sides. An abnormal communication between the right and left ventricles and shunt formation is the main mechanism of hemodynamic compromise in vsd. The defect can be small or large.